Role of nucleoid-associated proteins Hha and H-NS in expression of Salmonella enterica activators HilD, HilC, and RtsA required for cell invasion
- PMID: 17675384
- PMCID: PMC2045230
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00905-07
Role of nucleoid-associated proteins Hha and H-NS in expression of Salmonella enterica activators HilD, HilC, and RtsA required for cell invasion
Abstract
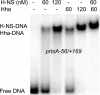
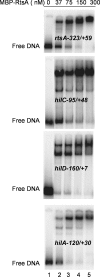
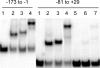
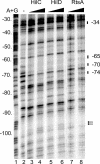
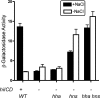
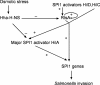
The coordinate expression of Salmonella enterica invasion genes on Salmonella pathogenicity island 1 is under the control of the complex circuits of regulation that involve the AraC/XylS family transcriptional activators HilD, HilC, and RtsA and nucleoid-associated proteins. Single-copy transcription fusions were used to assess the effects of nucleoid-associated proteins Hha and H-NS on hilD, hilC, and rtsA expression. The data show that all three genes, hilD, hilC, and rtsA, were repressed by H-NS and/or Hha. The repression of rtsA was the highest among tested genes. The level of rtsA-lac was equally elevated in hns and hha mutants and was further enhanced in the hns hha double mutant under low-osmolarity conditions. Electrophoretic mobility shift experiments showed that H-NS and Hha directly bind to the rtsA promoter. In addition to the negative control that was exerted by H-NS/Hha under low-osmolarity conditions, the homologous virulence activators HilD, HilC, and RtsA (Hil activators) induced rtsA-lac expression in a high-salt medium. A DNase footprinting assay of the rtsA promoter revealed one common DNA-binding site for all three Hil activators centered at position -54 relative to the transcriptional start site. In the absence of Hha and H-NS, however, osmoregulation of the rtsA promoter was lost, and Hil activators were not required for rtsA transcription. These results taken together suggest that the HilD, HilC, and RtsA proteins induce the transcription of the rtsA promoter by counteracting H-NS/Hha-mediated repression.
Figures
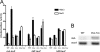
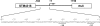

Similar articles
-
DNA-binding activities of the HilC and HilD virulence regulatory proteins of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.J Bacteriol. 2002 Aug;184(15):4148-60. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.15.4148-4160.2002. J Bacteriol. 2002. PMID: 12107132 Free PMC article.
-
HilD, HilC, and RtsA Form Homodimers and Heterodimers To Regulate Expression of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island I Type III Secretion System.J Bacteriol. 2020 Apr 9;202(9):e00012-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00012-20. Print 2020 Apr 9. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32041797 Free PMC article.
-
HilD, HilC and RtsA constitute a feed forward loop that controls expression of the SPI1 type three secretion system regulator hilA in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Aug;57(3):691-705. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04737.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16045614
-
Salmonella invasion gene regulation: a story of environmental awareness.J Microbiol. 2005 Feb;43 Spec No:110-7. J Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15765064 Review.
-
Adaptation to the host environment: regulation of the SPI1 type III secretion system in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;10(1):24-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.12.002. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17208038 Review.
Cited by
-
Two-component regulators control hilA expression by controlling fimZ and hilE expression within Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Infect Immun. 2015 Mar;83(3):978-85. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02506-14. Epub 2014 Dec 29. Infect Immun. 2015. PMID: 25547794 Free PMC article.
-
HilD induces expression of a novel Salmonella Typhimurium invasion factor, YobH, through a regulatory cascade involving SprB.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 4;9(1):12725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49192-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31484980 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into the regulation of foreign genes in Salmonella by the Hha/H-NS complex.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 10;288(19):13356-69. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.455378. Epub 2013 Mar 20. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23515315 Free PMC article.
-
Envelope Stress and Regulation of the Salmonella Pathogenicity Island 1 Type III Secretion System.J Bacteriol. 2020 Aug 10;202(17):e00272-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00272-20. Print 2020 Aug 10. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32571967 Free PMC article.
-
Intraspecies variation in the emergence of hyperinfectious bacterial strains in nature.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(4):e1002647. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002647. Epub 2012 Apr 12. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22511871 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbar, S., L. M. Schechter, C. P. Lostroh, and C. A. Lee. 2003. AraC/XylS family members, HilD and HilC, directly activate virulence gene expression independently of HilA in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 47:715-729. - PubMed
-
- Altier, C. 2005. Genetic and environmental control of Salmonella invasion. J. Microbiol. 43:85-92. - PubMed
-
- Atlung, T., and H. Ingmer. 1997. H-NS: a modulator of environmentally regulated gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 24:7-17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

