Generation of virulence factor variants in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms
- PMID: 17675387
- PMCID: PMC2168666
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00789-07
Generation of virulence factor variants in Staphylococcus aureus biofilms
Abstract
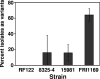
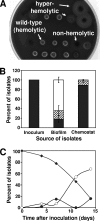
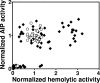
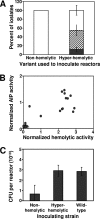
Several serious diseases are caused by biofilm-associated Staphylococcus aureus. Colonial variants occur in biofilms of other bacterial species, and S. aureus variants are frequently isolated from biofilm-associated infections. Thus, we studied the generation of variants with altered expression of virulence factors in S. aureus biofilms. We observed that the number of variants found in biofilms, as measured by hemolytic activity, varied for different strains. Further study of hemolytic activity and signaling by the accessory gene regulator (Agr) quorum-sensing system in one S. aureus strain revealed three primary biofilm subpopulations: nonhemolytic (Agr deficient), hemolytic (Agr positive), and hyperhemolytic (also Agr positive). The nonhemolytic variant became the numerically dominant subpopulation in the biofilm. The nonhemolytic variant phenotype was stable and heritable, indicating a genetic perturbation, whereas the hyperhemolytic phenotype was unstable, suggesting a phase variation. Transcription profiling revealed that expression of the agr locus and many extracellular virulence factors was repressed in the nonhemolytic variant. Expression of the agr-activating gene, sarU, was also repressed in the nonhemolytic variant, suggesting one potential regulatory pathway responsible for the Agr-deficient phenotype. We suggest that the development of these variants in biofilms may have important clinical implications.
Figures
References
-
- Akiyama, H., T. Hamada, W. K. Huh, O. Yamasaki, T. Oono, W. Fujimoto, and K. Iwatsuki. 2003. Confocal laser scanning microscopic observation of glycocalyx production by Staphylococcus aureus in skin lesions of bullous impetigo, atopic dermatitis, and pemphigus foliaceus. Br. J. Dermatol. 148:526-532. - PubMed
-
- Bergdoll, M. S., B. A. Crass, R. F. Reiser, R. N. Robbins, and J. P. Davis. 1981. A new staphylococcal enterotoxin, enterotoxin F, associated with toxic-shock-syndrome Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Lancet 1:1017-1021. - PubMed
-
- Bernheimer, A. W. 1988. Assay of hemolytic toxins. Methods Enzymol. 165:213-217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

