MarR-like transcriptional regulator involved in detoxification of aromatic compounds in Sulfolobus solfataricus
- PMID: 17675388
- PMCID: PMC2168448
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00885-07
MarR-like transcriptional regulator involved in detoxification of aromatic compounds in Sulfolobus solfataricus
Abstract
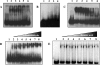
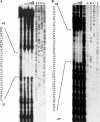
A DNA binding protein, BldR, was identified in the crenarchaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus as a protein 5- to 10-fold more abundant in cells grown in the presence of toxic aldehydes; it binds to regulatory sequences located upstream of an alcohol dehydrogenase gene (Sso2536). BldR is homologous to bacterial representatives of the MarR (multiple antibiotic resistance) family of transcriptional regulators that mediate response to multiple environmental stresses. Transcriptional analysis revealed that the bldR gene was transcribed in a bicistronic unit composed of the genes encoding the transcriptional regulator (Sso1352) and a putative multidrug transporter (Sso1351) upstream. By homology to bacterial counterparts, the bicistron was named the mar-like operon. The level of mar-like operon expression was found to be increased at least 10-fold in response to chemical stress by aromatic aldehydes. Under the same growth conditions, similar enhanced in vivo levels of Sso2536 gene transcript were also measured. The gene encoding BldR was expressed in E. coli, and the recombinant protein was purified to homogeneity. DNA binding assays demonstrated that the protein is indeed a transcription factor able to recognize site specifically both the Sso2536 and mar-like promoters at sites containing palindromic consensus sequences. Benzaldehyde, the substrate of ADH(Ss), stimulates DNA binding of BldR at both promoters. The role of BldR in the auto-activation as well as in the regulation of the Sso2536 gene, together with results of increased operon and gene expression under conditions of exposure to aromatic aldehydes, indicates a novel coordinate regulatory mechanism in cell defense against stress by aromatic compounds.
Figures



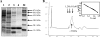

References
-
- Alekshun, M. N., S. B. Levy, T. R. Mealy, B. A. Seaton, and J. F. Head. 2001. The crystal structure of MarR, a regulator of multiple antibiotic resistance, at 2.3 A resolution. Nat. Struct. Biol. 8:710-714. - PubMed
-
- Bell, S. D., and S. P. Jackson. 2000. Mechanism of autoregulation by an archaeal transcriptional repressor. J. Biol. Chem. 275:31624-31629. - PubMed
-
- Bell, S. D., C. H. Botting, B. N. Wardleworth, S. P. Jackson, and M. F. White. 2002. The interaction of Alba, a conserved archaeal chromatin protein, with Sir2 and its regulation by acetylation. Science 296:148-151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

