The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB77 modulates auxin signal transduction
- PMID: 17675404
- PMCID: PMC2002618
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.107.050963
The Arabidopsis transcription factor MYB77 modulates auxin signal transduction
Abstract
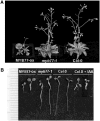
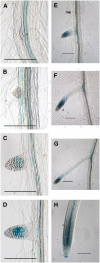
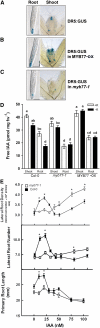
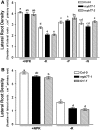
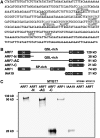
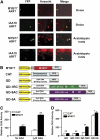
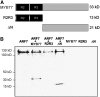
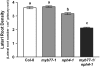
Auxin is a key plant hormone that regulates plant development, apical dominance, and growth-related tropisms, such as phototropism and gravitropism. In this study, we report a new Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor, MYB77, that is involved in auxin response. In MYB77 knockout plants, we found that auxin-responsive gene expression was greatly attenuated. Lateral root density in the MYB77 knockout was lower than the wild type at low concentrations of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and also under low nutrient conditions. MYB77 interacts with auxin response factors (ARFs) in vitro through the C terminus (domains III and IV) of ARFs and the activation domain of MYB77. A synergistic genetic interaction was demonstrated between MYB77 and ARF7 that resulted in a strong reduction in lateral root numbers. Experiments with protoplasts confirmed that the coexpression of MYB77 and an ARF C terminus enhance reporter gene expression. R2R3 MYB transcription factors have not been previously implicated in regulating the expression of auxin-inducible genes. Also it was previously unknown that ARFs interact with proteins other than those in the Aux/IAA family via conserved domains. The interaction between MYB77 and ARFs defines a new type of combinatorial transcriptional control in plants. This newly defined transcription factor interaction is part of the plant cells' repertoire for modulating response to auxin, thereby controlling lateral root growth and development under changing environmental conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Abel, S., Nguyen, M., and Theologis, A. (1995). The PS-IAA4/5-like family of early auxin-inducible mRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Mol. Biol. 251 533–549. - PubMed
-
- Berleth, T., Krogan, N.T., and Scarpella, E. (2004). Auxin signals—Turning genes on and turning cells around. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 7 553–563. - PubMed
-
- Blakeslee, J.J., Peer, W.A., and Murphy, A.S. (2005). Auxin transport. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 8 494–500. - PubMed
-
- Blilou, I., Xu, J., Wildwater, M., Willemsen, V., Paponov, I., Friml, J., Heidstra, R., Aida, M., Palme, K., and Scheres, B. (2005). The PIN auxin efflux facilitator network controls growth and patterning in Arabidopsis roots. Nature 433 39–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

