Unchecked CD70 expression on T cells lowers threshold for T cell activation in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 17675524
- PMCID: PMC2832914
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.4.2609
Unchecked CD70 expression on T cells lowers threshold for T cell activation in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
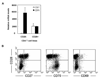
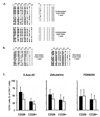
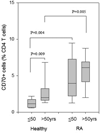
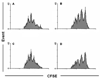
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by premature immune aging with accumulation of degenerate T cells deficient for CD28. Gene expression profiling of CD4(+)CD28(-) and CD4(+)CD28(+) T cells to discover disease-promoting activities of CD28(-) T cells identified expression of CD70 as a most striking difference. Hence, CD70 was significantly more expressed in CD4 T cells from RA patients compared with age-matched controls (p < 0.006). The underlying mechanism was a failure to repress CD70 expression after activation-dependent induction. This defect in RA was not related to differential promoter demethylation. CD70 on bystander CD4(+)CD28(-) T cells functioned by lowering the threshold for T cell activation; admixture of CD4(+)CD28(-) T cells augmented TCR-induced responses of autologous naive CD4(+)CD28(+) T cells, particularly of low-avidity T cells. The data support a model in which CD70 expressed on T cells causes degeneracy in T cell responses and undermines tolerance mechanisms that normally control T cell autoreactivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest
Figures



Similar articles
-
Decreased ERK and JNK signaling contribute to gene overexpression in "senescent" CD4+CD28- T cells through epigenetic mechanisms.J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Jan;87(1):137-45. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0809562. Epub 2009 Oct 20. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 19843577 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased DNA methyltransferase levels contribute to abnormal gene expression in "senescent" CD4(+)CD28(-) T cells.Clin Immunol. 2009 Aug;132(2):257-65. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2009.03.529. Epub 2009 Apr 25. Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19394279 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of 1,25(OH)2D3 and Vitamin D Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus by Regulating the Activation of CD4+ T Cells and the PKCδ/ERK Signaling Pathway.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(3-4):743-756. doi: 10.1159/000453135. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27915349
-
RFX1 regulates CD70 and CD11a expression in lupus T cells by recruiting the histone methyltransferase SUV39H1.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(6):R227. doi: 10.1186/ar3214. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 21192791 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of T-cell tolerance.Immunol Rev. 2011 May;241(1):133-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2011.01012.x. Immunol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21488895 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Expression of CD70 and CD27 Is Increased in Alopecia Areata Lesions and Associated with Disease Severity and Activity.Dermatol Res Pract. 2022 Mar 8;2022:5004642. doi: 10.1155/2022/5004642. eCollection 2022. Dermatol Res Pract. 2022. PMID: 35300124 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased ERK and JNK signaling contribute to gene overexpression in "senescent" CD4+CD28- T cells through epigenetic mechanisms.J Leukoc Biol. 2010 Jan;87(1):137-45. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0809562. Epub 2009 Oct 20. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 19843577 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Cytometry Analysis Reveals that Specific Intratumoral CD4+ T Cell Subsets Correlate with Patient Survival in Follicular Lymphoma.Cell Rep. 2019 Feb 19;26(8):2178-2193.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.085. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30784598 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CD70 and CD11a in immune thrombocytopenia patients.J Clin Immunol. 2011 Aug;31(4):632-42. doi: 10.1007/s10875-011-9539-1. Epub 2011 May 4. J Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21541792
-
Beyond TNF: TNF superfamily cytokines as targets for the treatment of rheumatic diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017 Apr;13(4):217-233. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.22. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28275260 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM. Rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2005;204:55–73. - PubMed
-
- Feldmann M, Maini RN. Anti-TNF alpha therapy of rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned? Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:163–196. - PubMed
-
- Schett G, Hayer S, Zwerina J, Redlich K, Smolen JS. Mechanisms of Disease: the link between RANKL and arthritic bone disease. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2005;1:47–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

