Bone hydatid disease
- PMID: 17675547
- PMCID: PMC2600110
- DOI: 10.1136/pgmj.2007.057166
Bone hydatid disease
Abstract
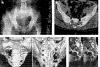
Bone hydatid disease lacks a typical clinical appearance and image characteristics on x ray or CT are similar to those of tuberculosis, metastases and giant cell tumour or bone cysts. However, MRI does show distinctive diagnostic features of bone hydatid disease, especially in the spine. Until recently, treatment of osseous hydatid disease has been entirely surgical. Effective chemotherapy using benzimidazoles, particularly mebendazole, albendazole and combination treatments, has now been achieved in experimental studies and clinical practice. However, most of these drugs are still in the experimental stage or are in the early stages of clinical use.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: none stated
References
-
- Szypryt E P, Morris D L, Mulholland R C. Combined chemotherapy and surgery for hydatid bone disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 198769141–144. - PubMed
-
- Gemmell M A, Lawson J R, Roberts M G. Towards global control of cystic and alveolar hydatid diseases. Parasitol Today 19873144–151. - PubMed
-
- Craig P S, Larrieu E. Control of cystic echinococcosis/hydatidosis: 1863–2002. Adv Parasitol 200661443–508. - PubMed
-
- Kammerer W S. Echinococcosis affecting the central nervous system. Semin Neurol 199313144–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical