A predicted interactome for Arabidopsis
- PMID: 17675552
- PMCID: PMC2048726
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.107.103465
A predicted interactome for Arabidopsis
Abstract
The complex cellular functions of an organism frequently rely on physical interactions between proteins. A map of all protein-protein interactions, an interactome, is thus an invaluable tool. We present an interactome for Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) predicted from interacting orthologs in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), nematode worm (Caenorhabditis elegans), fruitfly (Drosophila melanogaster), and human (Homo sapiens). As an internal quality control, a confidence value was generated based on the amount of supporting evidence for each interaction. A total of 1,159 high confidence, 5,913 medium confidence, and 12,907 low confidence interactions were identified for 3,617 conserved Arabidopsis proteins. There was significant coexpression of genes whose proteins were predicted to interact, even among low confidence interactions. Interacting proteins were also significantly more likely to be found within the same subcellular location, and significantly less likely to be found in conflicting localizations than randomly paired proteins. A notable exception was that proteins located in the Golgi were more likely to interact with Golgi, vacuolar, or endoplasmic reticulum sorted proteins, indicating possible docking or trafficking interactions. These predictions can aid researchers by extending known complexes and pathways with candidate proteins. In addition we have predicted interactions for many previously unknown proteins in known pathways and complexes. We present this interactome, and an online Web interface the Arabidopsis Interactions Viewer, as a first step toward understanding global signaling in Arabidopsis, and to whet the appetite for those who are awaiting results from high-throughput experimental approaches.
Figures
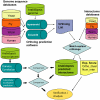





References
-
- Bhardwaj N, Lu H (2005) Correlation between gene expression profiles and protein-protein interactions within and across genomes. Bioinformatics 21 2730–2738 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

