High glucose-induced thioredoxin-interacting protein in renal proximal tubule cells is independent of transforming growth factor-beta1
- PMID: 17675577
- PMCID: PMC1959480
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060813
High glucose-induced thioredoxin-interacting protein in renal proximal tubule cells is independent of transforming growth factor-beta1
Abstract
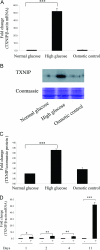
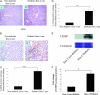
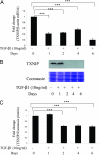
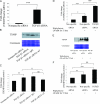
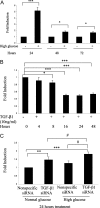
Hyperglycemia is a causative factor in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Here, we demonstrate the transcriptional profiles of the human proximal tubule cell line (HK-2 cells) exposed to high glucose using cDNA microarray analysis. Thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) was the gene most significantly increased among 10 strongly up-regulated and 15 down-regulated genes. Txnip, heat shock proteins 70 and 90, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 20, and matrix metalloproteinase-7 were chosen for verification of gene expression. Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction confirmed the mRNA expression levels of these five genes, consistent with microarray analysis. The increased protein expression of Txnip, CCL20, and MMP7 were also verified by Western blotting and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Increased expression of Txnip and of nitrotyrosine, as a marker of oxidative stress, were confirmed in vivo in diabetic Ren-2 rats. Subsequent studies focused on the dependence of Txnip expression on up-regulation of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta1 under high-glucose conditions. Overexpression of Txnip and up-regulation of Txnip promoter activity were observed in cells in which the TGF-beta1 gene was silenced in HK-2 cells using short interfering RNA technology. High glucose further increased both Txnip expression and its promoter activity in TGF-beta1 silenced cells compared with wild-type cells exposed to high glucose, suggesting that high glucose induced Txnip through a TGF-beta1-indepen-dent pathway.
Figures
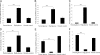
Similar articles
-
High glucose induces macrophage inflammatory protein-3 alpha in renal proximal tubule cells via a transforming growth factor-beta 1 dependent mechanism.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007 Nov;22(11):3147-53. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm365. Epub 2007 Jul 29. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007. PMID: 17664181
-
Knockdown of thioredoxin-interacting protein ameliorates high glucose-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial cells.Cell Signal. 2013 Dec;25(12):2788-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.009. Epub 2013 Sep 13. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 24041652
-
Upregulation of osteopontin gene expression in diabetic rat proximal tubular cells revealed by microarray profiling.Kidney Int. 2006 Mar;69(6):1005-15. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000206. Kidney Int. 2006. PMID: 16528250
-
Roles of thioredoxin binding protein (TXNIP) in oxidative stress, apoptosis and cancer.Mitochondrion. 2013 May;13(3):163-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2012.06.004. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Mitochondrion. 2013. PMID: 22750447 Review.
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein, hematopoietic stem cells, and hematopoiesis.Curr Opin Hematol. 2014 Jul;21(4):265-70. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000037. Curr Opin Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24686462 Review.
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein Deficiency Protects against Diabetic Nephropathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Dec;26(12):2963-77. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014050528. Epub 2015 Apr 8. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25855771 Free PMC article.
-
Early-outgrowth bone marrow cells attenuate renal injury and dysfunction via an antioxidant effect in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes.Diabetes. 2012 Aug;61(8):2114-25. doi: 10.2337/db11-1365. Epub 2012 May 17. Diabetes. 2012. PMID: 22596053 Free PMC article.
-
High glucose condition upregulated Txnip expression level in rat mesangial cells through ROS/MEK/MAPK pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Jan;347(1-2):175-82. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0626-z. Epub 2010 Oct 19. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 20953987
-
FXR expression is associated with dysregulated glucose and lipid levels in the offspring kidney induced by maternal obesity.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015 Nov 14;12:40. doi: 10.1186/s12986-015-0032-3. eCollection 2015. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26583035 Free PMC article.
-
Plumbagin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy via interruption of pathways that include NOX4 signalling.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 26;8(8):e73428. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073428. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23991195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gilbert RE, Cooper ME. The tubulointerstitium in progressive diabetic kidney disease: more than an aftermath of glomerular injury? Kidney Int. 1999;56:1627–1637. - PubMed
-
- Phillips AO, Steadman R. Diabetic nephropathy: the central role of renal proximal tubular cells in tubulointerstitial injury. Histol Histopathol. 2002;17:247–252. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi T, Inoue T, Okada H, Kikuta T, Kanno Y, Nishida T, Takigawa M, Sugaya T, Suzuki H. Connective tissue growth factor mediates the profibrotic effects of transforming growth factor-β produced by tubular epithelial cells in response to high glucose. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2005;9:114–121. - PubMed
-
- Panchapakesan U, Pollock CA, Chen XM. The effect of high glucose and PPAR-gamma agonists on PPAR-γ expression and function in HK-2 cells. Am J Physiol. 2004;287:F528–F534. - PubMed
-
- Schulze PC, Yoshioka J, Takahashi T, He Z, King GL, Lee RT. Hyperglycemia promotes oxidative stress through inhibition of thioredoxin function by thioredoxin-interacting protein. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:30369–30374. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

