In vivo dynamics of RNA polymerase II transcription
- PMID: 17676063
- PMCID: PMC4942130
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb1280
In vivo dynamics of RNA polymerase II transcription
Abstract
We imaged transcription in living cells using a locus-specific reporter system, which allowed precise, single-cell kinetic measurements of promoter binding, initiation and elongation. Photobleaching of fluorescent RNA polymerase II revealed several kinetically distinct populations of the enzyme interacting with a specific gene. Photobleaching and photoactivation of fluorescent MS2 proteins used to label nascent messenger RNAs provided sensitive elongation measurements. A mechanistic kinetic model that fits our data was validated using specific inhibitors. Polymerases elongated at 4.3 kilobases min(-1), much faster than previously documented, and entered a paused state for unexpectedly long times. Transcription onset was inefficient, with only 1% of polymerase-gene interactions leading to completion of an mRNA. Our systems approach, quantifying both polymerase and mRNA kinetics on a defined DNA template in vivo with high temporal resolution, opens new avenues for studying regulation of transcriptional processes in vivo.
Figures
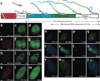



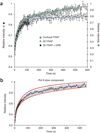
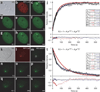
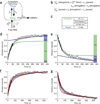

Comment in
-
RNA polymerase II transcription in living color.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007 Sep;14(9):788-90. doi: 10.1038/nsmb0907-788. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17823607 No abstract available.
References
-
- Moore MJ. From birth to death: the complex lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science. 2005;309:1514–1518. - PubMed
-
- Shilatifard A, Conaway RC, Conaway JW. The RNA polymerase II elongation complex. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2003;72:693–715. - PubMed
-
- Cramer P, Bushnell DA, Kornberg RD. Structural basis of transcription: RNA polymerase II at 2.8 angstrom resolution. Science. 2001;292:1863–1876. - PubMed
-
- Cramer P. RNA polymerase II structure: from core to functional complexes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004;14:218–226. - PubMed
-
- Krumm A, Hickey LB, Groudine M. Promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II defines a general rate-limiting step after transcription initiation. Genes Dev. 1995;9:559–572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

