Cardiotoxicity of Ma Huang/caffeine or ephedrine/caffeine in a rodent model system
- PMID: 17676524
- PMCID: PMC2104562
- DOI: 10.1080/01926230701459978
Cardiotoxicity of Ma Huang/caffeine or ephedrine/caffeine in a rodent model system
Abstract
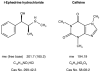
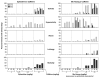
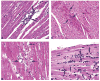
Ma Huang (equivalent to 0, 12.5, 25, or 50 mg/kg ephedrine) or ephedrine (0, 6.25, 12.5, 25 mg/kg) were administered as one bolus oral dose to male F344 rats with and without caffeine. The herbal medicine Ma Huang (ephedra) in combination with caffeine caused rapid clinical signs of toxicity including salivation, hyperactivity, ataxia, and eventually lethargy, and failure to respond to stimuli. When this syndrome of clinical signs emerged, animals were moribund sacrificed, and a histological analysis for heart lesions performed. Cardiotoxicity included hemorrhage, necrosis, and degeneration in the ventricles or interventricular septum within 2-4 hours after treatment with Ma Huang (ephedra)/caffeine or ephedrine (the principal active component in Ma Huang)/caffeine. There was a steep dose response curve for cardiotoxicity with minimal toxicity seen at levels of Ma Huang (equivalent to 12.5 mg/kg ephedrine) with caffeine. However, cardiotoxic lesions occurred in 28% of animals with Ma Huang dosages equivalent to 25 mg/kg ephedrine with 15 or 30 mg/kg caffeine, and in 90% of animals at Ma Huang exposures equivalent to 50 mg/kg ephedrine with 15 or 30 mg/kg caffeine. Cardiotoxic lesions occurred in 47% of animals in the 25 mg/kg ephedrine groups with caffeine at 7.25, 15, or 30 mg/kg. There was no statistical difference in the occurrence of cardiotoxic lesions when 15 or 30 mg/kg caffeine was combined with Ma Huang equivalent to 25 or 50 mg/kg ephedrine; likewise there was no statistical difference in the occurrence of cardiotoxic lesions when 7.25, 15, or 30 mg/kg caffeine was combined with 25 mg/kg ephedrine. These results show that the cardiotoxic effects of the herbal medicine, Ma Huang, are similar to that of ephedrine, the principal active ingredient in the herbal medicine. The combination of Ma Huang or ephedrine with caffeine enhanced the cardiotoxicity over that with the herbal medicine or the active ingredient alone.
Figures

References
-
- Astrup A, Toubro S, Cannon S, Hein P, Madsen J. Thermogenic synergism between ephedrine and caffeine in healthy volunteers: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Metabolism. 1991;40:323–9. - PubMed
-
- Braun FJ, Broad LM, Armstrong DL, Putney JW., Jr Stable activation of single Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ channels in divalent cation-free solutions. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:1063–70. - PubMed
-
- Broad LM, Braun FJ, Lievremont JP, Bird GSJ, Kurosaki T, Putney JW., Jr Role of the phospholipase C-inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate pathway in calcium release-activated calcium current and capacitative calcium entry. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:15945–52. - PubMed
-
- Burt RP. Depletion of Ca from intracelluar stores potentiates spontaneous contractions of the rat portal ven. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;496:109–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

