Interactions that drive Sec-dependent bacterial protein transport
- PMID: 17676771
- PMCID: PMC2675607
- DOI: 10.1021/bi7010064
Interactions that drive Sec-dependent bacterial protein transport
Abstract
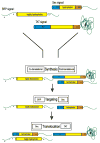
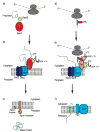
Understanding the transport of hydrophilic proteins across biological membranes continues to be an important undertaking. The general secretory (Sec) pathway in Escherichia coli transports the majority of E. coli proteins from their point of synthesis in the cytoplasm to their sites of final localization, associating sequentially with a number of protein components of the transport machinery. The targeting signals for these substrates must be discriminated from those of proteins transported via other pathways. While targeting signals for each route have common overall characteristics, individual signal peptides vary greatly in their amino acid sequences. How do these diverse signals interact specifically with the proteins that comprise the appropriate transport machinery and, at the same time, avoid targeting to an alternate route? The recent publication of the crystal structures of components of the Sec transport machinery now allows a more thorough consideration of the interactions of signal sequences with these components.
Figures

References
-
- Engelman DM, Steitz TA. The spontaneous insertion of proteins into and across membranes: the helical hairpin hypothesis. Cell. 1981;23:411–422. - PubMed
-
- Luirink J, von Heijne G, Houben E, de Gier JW. Biogenesis of inner membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2005;59:329–355. - PubMed
-
- Chen M, Samuelson JC, Jiang F, Muller M, Kuhn A, Dalbey RE. Direct interaction of YidC with the Sec-independent Pf3 coat protein during its membrane protein insertion. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:7670–7675. - PubMed
-
- Sargent F, Berks BC, Palmer T. Pathfinders and trailblazers: a prokaryotic targeting system for transport of folded proteins. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006;254:198–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

