Construction of miniantibodies for the in vivo study of human autoimmune diseases in animal models
- PMID: 17678525
- PMCID: PMC1963447
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-7-46
Construction of miniantibodies for the in vivo study of human autoimmune diseases in animal models
Abstract
Background: Phage display antibody libraries have been made from the lymphocytes of patients suffering from autoimmune diseases in which the antibodies are known to play a role in the pathogenesis or are important for the diagnosis of the disease. In the case of Celiac Disease, the immune response is directed against the autoantigen tissue transglutaminase. However, despite numerous studies, the role of these antibodies in the pathogenesis of this disease has not been elucidated.
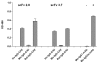
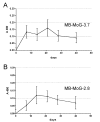
Results: We were able to engineer specific anti-transglutaminase antibody fragments in the form called "miniantibody". These are produced by genetic fusion of anti-tTG scFv to Human, Mouse or Rat Fc domains, making them suitable for in vivo expression. The results obtained here indicate that the miniantibody molecule is efficiently secreted, and that the reactivity to the antigen is retained even after fusion to heterologous Fc domains. Further analysis demonstrate that the molecule is secreted as homodimeric, mimicking original antibody structure. Finally, the in vivo expression in mice leads to detectable serum levels with no apparent gross immune response by the host.
Conclusion: In this work we demonstrated the usefulness of a method for the in vivo expression of miniantibodies specific to transglutaminase, corresponding to the autoimmune specificity of Celiac Disease. This can be proposed as a general method to study the pathogenic role of autoimmune antibodies in autoimmune diseases.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

