Fibroblast growth factor homologous factors control neuronal excitability through modulation of voltage-gated sodium channels
- PMID: 17678857
- PMCID: PMC2974323
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.006
Fibroblast growth factor homologous factors control neuronal excitability through modulation of voltage-gated sodium channels
Abstract
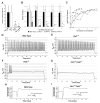
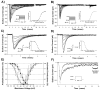
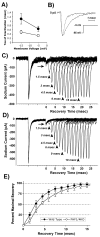
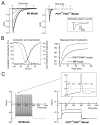
Neurons integrate and encode complex synaptic inputs into action potential outputs through a process termed "intrinsic excitability." Here, we report the essential contribution of fibroblast growth factor homologous factors (FHFs), a family of voltage-gated sodium channel binding proteins, to this process. Fhf1-/-Fhf4-/- mice suffer from severe ataxia and other neurological deficits. In mouse cerebellar slice recordings, WT granule neurons can be induced to fire action potentials repetitively (approximately 60 Hz), whereas Fhf1-/-Fhf4-/- neurons often fire only once and at an elevated voltage spike threshold. Sodium channels in Fhf1-/-Fhf4-/- granule neurons inactivate at more negative membrane potential, inactivate more rapidly, and are slower to recover from the inactivated state. Altered sodium channel physiology is sufficient to explain excitation deficits, as tested in a granule cell computer model. These findings offer a physiological mechanism underlying human spinocerebellar ataxia induced by Fhf4 mutation and suggest a broad role for FHFs in the control of excitability throughout the CNS.
Figures
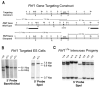
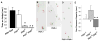
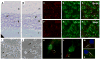
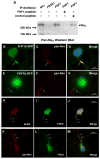
References
-
- Ahern CA, Zhang JF, Wookalis MJ, Horn R. Modulation of the cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5 by Fyn, a Src family tyrosine kinase. Circ Res. 2005;96:991–998. - PubMed
-
- An RH, Wang XL, Kerem B, Benhorin J, Medina A, Goldmit M, Kass RS. Novel LQT-3 mutation affects Na+ channel activity through interactions between alpha- and beta1-subunits. Circ Res. 1998;83:141–146. - PubMed
-
- Boiko T, Rasband MN, Levinson SR, Caldwell JH, Mandel G, Trimmer JS, Matthews G. Compact myelin dictates the differential targeting of two sodium channel isoforms in the same axon. Neuron. 2001;30:91–104. - PubMed
-
- Cantrell AR, Catterall WA. Neuromodulation of Na+ channels: an unexpected form of cellular plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001;2:397–407. - PubMed
-
- Casado M, Isope P, Ascher P. Involvement of presynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in cerebellar long-term depression. Neuron. 2002;33:123–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

