Differential effects of human SP-A1 and SP-A2 variants on phospholipid monolayers containing surfactant protein B
- PMID: 17678872
- PMCID: PMC2964661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.06.025
Differential effects of human SP-A1 and SP-A2 variants on phospholipid monolayers containing surfactant protein B
Abstract
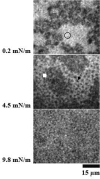
Surfactant protein A (SP-A), the most abundant protein in the lung alveolar surface, has multiple activities, including surfactant-related functions. SP-A is required for the formation of tubular myelin and the lung surface film. The human SP-A locus consists of two functional SP-A genes, SP-A1 and SP-A2, with a number of alleles characterized for each gene. We have found that the human in vitro expressed variants, SP-A1 (6A(2)) and SP-A2 (1A(0)), and the coexpressed SP-A1/SP-A2 (6A(2)/1A(0)) protein have a differential influence on the organization of phospholipid monolayers containing surfactant protein B (SP-B). Lipid films containing SP-B and SP-A2 (1A(0)) showed surface features similar to those observed in lipid films with SP-B and native human SP-A. Fluorescence images revealed the presence of characteristic fluorescent probe-excluding clusters coexisting with the traditional lipid liquid-expanded and liquid-condensed phase. Images of the films containing SP-B and SP-A1 (6A(2)) showed different distribution of the proteins. The morphology of lipid films containing SP-B and the coexpressed SP-A1/SP-A2 (6A(2)/1A(0)) combined features of the individual films containing the SP-A1 or SP-A2 variant. The results indicate that human SP-A1 and SP-A2 variants exhibit differential effects on characteristics of phospholipid monolayers containing SP-B. This may differentially impact surface film activity.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Genetic complexity of the human innate host defense molecules, surfactant protein A1 (SP-A1) and SP-A2--impact on function.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2009;19(2):125-37. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v19.i2.30. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2009. PMID: 19392648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survival of Surfactant Protein-A1 and SP-A2 Transgenic Mice After Klebsiella pneumoniae Infection, Exhibits Sex-, Gene-, and Variant Specific Differences; Treatment With Surfactant Protein Improves Survival.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 16;9:2404. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02404. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30459763 Free PMC article.
-
Human Pulmonary Surfactant Protein SP-A1 Provides Maximal Efficiency of Lung Interfacial Films.Biophys J. 2016 Aug 9;111(3):524-536. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2016.06.025. Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 27508436 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of surfactant protein A on regional organization of phospholipid monolayers containing surfactant protein B or C.Biophys J. 2000 Oct;79(4):2010-23. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76449-6. Biophys J. 2000. PMID: 11023905 Free PMC article.
-
Human Surfactant Protein SP-A1 and SP-A2 Variants Differentially Affect the Alveolar Microenvironment, Surfactant Structure, Regulation and Function of the Alveolar Macrophage, and Animal and Human Survival Under Various Conditions.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 17;12:681639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.681639. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in the alveolar macrophage proteome in transgenic mice expressing human SP-A1 and SP-A2.J Proteom Genom Res. 2013 Apr 1;1(2):2-26. doi: 10.14302/issn.2326-0793.jpgr-12-207. J Proteom Genom Res. 2013. PMID: 24729982 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of Drosha in human alveolar type II cells alters expression of SP-A in culture: a pilot study.Exp Lung Res. 2014 Sep;40(7):354-66. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2014.929757. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Exp Lung Res. 2014. PMID: 25058539 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic complexity of the human innate host defense molecules, surfactant protein A1 (SP-A1) and SP-A2--impact on function.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2009;19(2):125-37. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v19.i2.30. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2009. PMID: 19392648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cap-independent translation of human SP-A 5'-UTR variants: a double-loop structure and cis-element contribution.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009 Apr;296(4):L635-47. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90508.2008. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19181744 Free PMC article.
-
IL-18R1 and IL-18RAP SNPs may be associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia in African-American infants.Pediatr Res. 2012 Jan;71(1):107-14. doi: 10.1038/pr.2011.14. Pediatr Res. 2012. PMID: 22289858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yu S, Harding PG, Smith N, Possmayer F. Bovine pulmonary surfactant: chemical composition and physical properties. Lipids. 1983;18:522–9. - PubMed
-
- Rice WR, Ross GF, Singleton FM, Dingle S, Whitsett JA. Surfactant-associated protein inhibits phospholipid secretion from type II cells. J Appl Physiol. 1987;63:692–8. - PubMed
-
- Jain D, Dodia C, Bates SR, Hawgood S, Poulain FR, Fisher AB. SP-A is necessary for increased clearance of alveolar DPPC with hyperventilation or secretagogues. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003;284:L759–65. - PubMed
-
- Benson BJ, Williams MC, Sueishi K, Goerke J, Sargeant T. Role of calcium ions the structure and function of pulmonary surfactant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984;793:18–27. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki Y, Fujita Y, Kogishi K. Reconstitution of tubular myelin from synthetic lipids and proteins associated with pig pulmonary surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;140:75–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

