Brain surface conformal parameterization using Riemann surface structure
- PMID: 17679336
- PMCID: PMC3197830
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2007.895464
Brain surface conformal parameterization using Riemann surface structure
Abstract
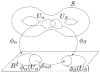
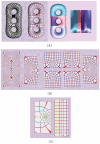
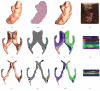
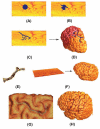
In medical imaging, parameterized 3-D surface models are useful for anatomical modeling and visualization, statistical comparisons of anatomy, and surface-based registration and signal processing. Here we introduce a parameterization method based on Riemann surface structure, which uses a special curvilinear net structure (conformal net) to partition the surface into a set of patches that can each be conformally mapped to a parallelogram. The resulting surface subdivision and the parameterizations of the components are intrinsic and stable (their solutions tend to be smooth functions and the boundary conditions of the Dirichlet problem can be enforced). Conformal parameterization also helps transform partial differential equations (PDEs) that may be defined on 3-D brain surface manifolds to modified PDEs on a two-dimensional parameter domain. Since the Jacobian matrix of a conformal parameterization is diagonal, the modified PDE on the parameter domain is readily solved. To illustrate our techniques, we computed parameterizations for several types of anatomical surfaces in 3-D magnetic resonance imaging scans of the brain, including the cerebral cortex, hippocampi, and lateral ventricles. For surfaces that are topologically homeomorphic to each other and have similar geometrical structures, we show that the parameterization results are consistent and the subdivided surfaces can be matched to each other. Finally, we present an automatic sulcal landmark location algorithm by solving PDEs on cortical surfaces. The landmark detection results are used as constraints for building conformal maps between surfaces that also match explicitly defined landmarks.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brain surface parameterization using Riemann surface structure.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2005;8(Pt 2):657-65. doi: 10.1007/11566489_81. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2005. PMID: 16686016
-
Brain surface conformal parameterization with algebraic functions.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2006;9(Pt 2):946-54. doi: 10.1007/11866763_116. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2006. PMID: 17354864
-
Optimization of brain conformal mapping with landmarks.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2005;8(Pt 2):675-83. doi: 10.1007/11566489_83. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2005. PMID: 16686018 Clinical Trial.
-
Brain functional localization: a survey of image registration techniques.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2007 Apr;26(4):427-51. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2007.892508. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17427731 Review.
-
Computational anatomy with the SPM software.Magn Reson Imaging. 2009 Oct;27(8):1163-74. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2009.01.006. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Magn Reson Imaging. 2009. PMID: 19249168 Review.
Cited by
-
Federated Morphometry Feature Selection for Hippocampal Morphometry Associated Beta-Amyloid and Tau Pathology.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 25;15:762458. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.762458. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34899166 Free PMC article.
-
Applying surface-based morphometry to study ventricular abnormalities of cognitively unimpaired subjects prior to clinically significant memory decline.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102338. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102338. Epub 2020 Jul 5. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32683323 Free PMC article.
-
INVESTIGATING THE EFFECT OF TAU DEPOSITION AND APOE ON HIPPOCAMPAL MORPHOMETRY IN ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE: A FEDERATED CHOW TEST MODEL.Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2022 Mar;2022:10.1109/isbi52829.2022.9761576. doi: 10.1109/isbi52829.2022.9761576. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Proc IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36147309 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Plasticity of the Hippocampus and Amygdala Induced by Electroconvulsive Therapy in Major Depression.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Feb 15;79(4):282-92. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.02.029. Epub 2015 Mar 5. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 25842202 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative characterization of the human retinotopic map based on quasiconformal mapping.Med Image Anal. 2022 Jan;75:102230. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.102230. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Med Image Anal. 2022. PMID: 34666194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thompson PM, Giedd JN, Woods RP, MacDonald D, Evans AC, Toga AW. Growth patterns in the developing human brain detected using continuum-mechanical tensor mapping. Nature. 2000 Mar.vol. 404(no. 6774):190–193. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y, Chiang M-C, Thompson PM. Automated surface matching using mutual information applied to Riemann surface structures; Proc. Med. Image Comp. Comput.-Assist. Intervention Part II; Palm Springs, CA. Oct. 2005.pp. 666–674. - PubMed
-
- Osher S, Sethian JA. Fronts propoagating with curvature dependent speed: Algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 1988;vol. 79:12–49.
-
- Mémoli F, Sapiro G, Thompson P. Implicit brain imaging. NeuroImage. 2004;vol. 23:S179–S188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

