Prostaglandin E2 modulates dendritic cell function during chlamydial genital infection
- PMID: 17680801
- PMCID: PMC2433296
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02642.x
Prostaglandin E2 modulates dendritic cell function during chlamydial genital infection
Abstract
Inflammatory responses mediated by antigen-presenting dendritic cells (DCs), can be modulated by the presence of prostaglandins (PG), including prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). PGE2 modifies the production of an immune response by altering DC function through PGE2 receptors. PGE2 is produced by epithelial cells lining the murine female reproductive tract during Chlamydia muridarum infection and likely manipulates the antichlamydial immune response during antigen uptake in the genital mucosa. Our data demonstrate that the PGE2 present locally in the genital tract upon chlamydial genital infection enhanced the recruitment of CD11b+ conventional DCs, but not CD45R+ plasmacytoid DCs, to infected genital tract tissue and draining lymph nodes in vivo. Furthermore, exposure to PGE2 in vitro during infection of murine bone-marrow-derived conventional DCs (cDCs) boosted interleukin-10 mRNA and protein while not influencing interleukin-12p40 production. Infection of cDCs markedly increased mRNA production of the costimulatory molecules CD86, CD40 and a member of the C-type lectin family, DEC-205, but addition of PGE2 increased other costimulatory molecules and C-type lectins. Also, exposure of PGE2 to infected cDCs increased FcgammaRIII and FcgammaRIIb, suggesting that PGE2 enhances the uptake and presentation of C. muridarum and augments production of the antichlamydial adaptive immune response. Taken together, the data suggest that exposure of infected cDCs to PGE2 drives production of a diverse adaptive immune response with implications for regulating tissue inflammation.
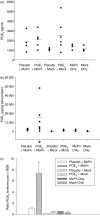
Figures





References
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services DoSP. MMWR. Vol. 51. Atlanta, GA: 2002. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Sexually Transmitted Disease 2003. RR-6.
-
- Brunham RC, Pourbohloul B, Mak S, White R, Rekart ML. The unexpected impact of a Chlamydia trachomatis infection control program on susceptibility to reinfection. J Infect Dis. 2005;192:1836–44. - PubMed
-
- Brunham RC, Rey-Ladino J. Immunology of Chlamydia infection: implications for a Chlamydia trachomatis vaccine. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:149–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

