A scientific journey through the 2-5A/RNase L system
- PMID: 17681844
- PMCID: PMC2075094
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2007.06.012
A scientific journey through the 2-5A/RNase L system
Abstract
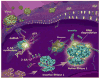
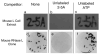
The antiviral and antitumor actions of interferons are caused, in part, by a remarkable regulated RNA cleavage pathway known as the 2-5A/RNase L system. 2'-5' linked oligoadenylates (2-5A) are produced from ATP by interferon-inducible synthetases. 2-5A activates pre-existing RNase L, resulting in the cleavage of RNAs within single-stranded regions. Activation of RNase L by 2-5A leads to an antiviral response, although precisely how this happens is a subject of ongoing investigations. Recently, RNase L was identified as the hereditary prostate cancer 1 gene. That finding has led to the discovery of a novel human retrovirus, XMRV. My scientific journey through the 2-5A system recounts some of the highlights of these efforts. Knowledge gained from studies on the 2-5A system could have an impact on development of therapies for important viral pathogens and cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A convenient and sensitive fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay for RNase L and 2',5' oligoadenylates.Methods Mol Med. 2005;116:103-13. doi: 10.1385/1-59259-939-7:103. Methods Mol Med. 2005. PMID: 16000857
-
The 2-5A system in viral infection and apoptosis.Biomed Pharmacother. 1998;52(9):386-90. doi: 10.1016/s0753-3322(99)80006-7. Biomed Pharmacother. 1998. PMID: 9856285 Review.
-
A transcriptional signaling pathway in the IFN system mediated by 2'-5'-oligoadenylate activation of RNase L.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Oct 11;102(41):14533-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507551102. Epub 2005 Oct 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16203993 Free PMC article.
-
Fascination with 2-5A-dependent RNase: a unique enzyme that functions in interferon action.J Interferon Res. 1994 Jun;14(3):101-4. doi: 10.1089/jir.1994.14.101. J Interferon Res. 1994. PMID: 7523539 Review.
-
An apoptotic signaling pathway in the interferon antiviral response mediated by RNase L and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 9;279(2):1123-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305893200. Epub 2003 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14570908
Cited by
-
Expression, purification and characterization of the interferon-inducible, antiviral and tumour-suppressor protein, human RNase L.J Biosci. 2012 Mar;37(1):103-13. doi: 10.1007/s12038-011-9180-4. J Biosci. 2012. PMID: 22357208
-
Overlapping Patterns of Rapid Evolution in the Nucleic Acid Sensors cGAS and OAS1 Suggest a Common Mechanism of Pathogen Antagonism and Escape.PLoS Genet. 2015 May 5;11(5):e1005203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005203. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25942676 Free PMC article.
-
Is XMRV a causal virus for prostate cancer?Asian J Androl. 2011 Sep;13(5):698-701. doi: 10.1038/aja.2011.32. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Asian J Androl. 2011. PMID: 21765437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNase L Suppresses Androgen Receptor Signaling, Cell Migration and Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Prostate Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 1;18(3):529. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030529. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28257035 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional response to VZV infection is modulated by RNA polymerase III in lung epithelial cell lines.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jul 25;12:943587. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.943587. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35959363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD. How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–64. - PubMed
-
- Mashimo T, Glaser P, Lucas M, Simon-Chazottes D, Ceccaldi PE, Montagutelli X, et al. Structural and functional genomics and evolutionary relationships in the cluster of genes encoding murine 2′,5′-oligoadenylate synthetases. Genomics. 2003;82:537–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

