The role of a probiotics mixture in the treatment of childhood constipation: a pilot study
- PMID: 17683583
- PMCID: PMC2148043
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2891-6-17
The role of a probiotics mixture in the treatment of childhood constipation: a pilot study
Abstract
Background: Inconsistent data exist about the efficacy of probiotics in the treatment of constipation. Several studies in adults with constipation showed positive effects of probiotics on constipation. Inconsistent data exist regarding the effect of a single probiotic strain in constipated children. The aim of this pilot study was to determine the effect of a mixture of probiotics containing bifidobacteria and lactobacilli in the treatment of childhood constipation.
Methods: Children aged 4-16 years with constipation as defined by the Rome III criteria were eligible for the study. During a 4 week period, children received a daily mix of 4 x 109 colony forming units of a probiotic mixture (Ecologic(R)Relief) containing Bifidobacteria (B.) bifidum, B. infantis, B. longum, Lactobacilli (L.) casei, L. plantarum and L. rhamnosus. Primary outcome measures were frequency of bowel movements (BMs) per week and stool consistency. Secondary outcome measures were number of faecal incontinence episodes per week, abdominal pain and side effects.
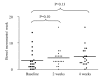
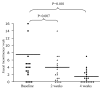
Results: Twenty children, 50% male, median age 8 (range 4-16) were included. The frequency of BMs per week increased from 2.0 (1.0-5.0) to 4.2 (0.0-16.0) in week 2 (p = 0.10) and 3.8 (2.1-7.0) in week 4 (p = 0.13). In 12 children presenting with <3 BMs/week, BMs per week increased significantly from 1.0 (0.0-2.0) to 3.0 (0.0-7.0) in week 2 (p = 0.01) and 3.0 (0.0-10.0) in week 4 (p = 0.01). The stool consistency was reported as hard in 7 children at baseline, in 4 children at week 2 (p = 0.23) and in 6 children after 4 weeks of treatment (p = 1.00). A significant decrease in number of faecal incontinence episodes per week was found in the entire group: 4.0 (0.0-35.0) to 1.5 (0.0-14.0) in week 2 (p = 0.01) and 0.3 (0.0-7.0) in week 4 (p = 0.001). The presence of abdominal pain decreased significantly from 45% to 25% in week 2 (p = 0.04) and 20% at week 4 (p = 0.006). No side effects were reported.
Conclusion: This pilot study shows that a mixture of probiotics, has positive effects on symptoms of constipation. To confirm these findings, a large randomised placebo controlled trial is required.
Figures
References
-
- Loening-Baucke V. Chronic constipation in children. Gastroenterology. 1993;105:1557–1564. - PubMed
-
- Voskuijl W, de Lorijn F, Verwijs W, Hogeman P, Heijmans J, Makel W, Taminiau J, Benninga M. PEG 3350 (Transipeg) versus lactulose in the treatment of childhood functional constipation: a double blind, randomised, controlled, multicentre trial. Gut. 2004;53:1590–1594. doi: 10.1136/gut.2004.043620. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical