STAT dynamics
- PMID: 17683973
- PMCID: PMC2683581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2007.06.021
STAT dynamics
Abstract
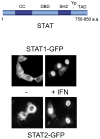
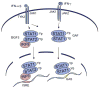
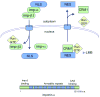
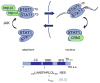
The ability of transcription factors to gain entrance to the nucleus is critical to their role in gene expression. Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs) are latent DNA binding factors activated by specific tyrosine phosphorylation. There are seven mammalian STAT genes encoding proteins that display constitutive nuclear localization and/or conditional nuclear localization. This review will focus on STAT1 and STAT2 that are activated in response to interferon and exhibit conditional nuclear localization. The dynamic redistribution of STAT1 and STAT2 between the cytoplasm and the nucleus is coordinate with their gain of ability to bind DNA.
Figures
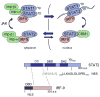
References
-
- Fu XY. A transcription factor with SH2 and SH3 domains is directly activated by an interferon alpha-induced cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase(s) Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):323–35. - PubMed
-
- Schindler C, Shuai K, Prezioso VR, Darnell JE., Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor [see comments] Science. 1992;257(5071):809–13. - PubMed
-
- Barbieri G, Velazquez L, Scrobogna M, Fellous M, Pellegrini S. Activation of the protein tyrosine kinase tyk2 by interferon alpha/beta. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jul 15;223(2):427–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

