Substantia nigra/ventral tegmental reward prediction error disruption in psychosis
- PMID: 17684497
- PMCID: PMC2564111
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002058
Substantia nigra/ventral tegmental reward prediction error disruption in psychosis
Abstract
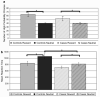
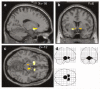
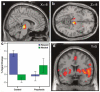
While dopamine systems have been implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and psychosis for many years, how dopamine dysfunction generates psychotic symptoms remains unknown. Recent theoretical interest has been directed at relating the known role of midbrain dopamine neurons in reinforcement learning, motivational salience and prediction error to explain the abnormal mental experience of psychosis. However, this theoretical model has yet to be explored empirically. To examine a link between psychotic experience, reward learning and dysfunction of the dopaminergic midbrain and associated target regions, we asked a group of first episode psychosis patients suffering from active positive symptoms and a group of healthy control participants to perform an instrumental reward conditioning experiment. We characterized neural responses using functional magnetic resonance imaging. We observed that patients with psychosis exhibit abnormal physiological responses associated with reward prediction error in the dopaminergic midbrain, striatum and limbic system, and we demonstrated subtle abnormalities in the ability of psychosis patients to discriminate between motivationally salient and neutral stimuli. This study provides the first evidence linking abnormal mesolimbic activity, reward learning and psychosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brain responses to different types of salience in antipsychotic naïve first episode psychosis: An fMRI study.Transl Psychiatry. 2018 Sep 21;8(1):196. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0250-3. Transl Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 30242202 Free PMC article.
-
Expected value and prediction error abnormalities in depression and schizophrenia.Brain. 2011 Jun;134(Pt 6):1751-64. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr059. Epub 2011 Apr 10. Brain. 2011. PMID: 21482548
-
Abnormal reward prediction-error signalling in antipsychotic naive individuals with first-episode psychosis or clinical risk for psychosis.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018 Jul;43(8):1691-1699. doi: 10.1038/s41386-018-0056-2. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2018. PMID: 29748629 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of receptors for insulin and leptin in the ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra (VTA/SN) of the rat: Historical perspective.Brain Res. 2016 Aug 15;1645:68-70. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.041. Epub 2015 Dec 28. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26731335 Review.
-
Involvement of basal ganglia and orbitofrontal cortex in goal-directed behavior.Prog Brain Res. 2000;126:193-215. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(00)26015-9. Prog Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11105648 Review.
Cited by
-
Auditory mismatch impairments are characterized by core neural dysfunctions in schizophrenia.Brain. 2015 May;138(Pt 5):1410-23. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv049. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Brain. 2015. PMID: 25743635 Free PMC article.
-
Anhedonia and ambivalence in schizophrenic patients with fronto-cerebellar metabolic abnormalities: a fluoro-d-glucose positron emission tomography study.Psychiatry Investig. 2009 Jun;6(2):72-7. doi: 10.4306/pi.2009.6.2.72. Epub 2009 Jun 30. Psychiatry Investig. 2009. PMID: 20046378 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Instructed Fear Learning in Delusion-Proneness.Front Psychol. 2022 Apr 13;13:786778. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.786778. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35496229 Free PMC article.
-
Social Mindfulness and Psychosis: Neural Response to Socially Mindful Behavior in First-Episode Psychosis and Patients at Clinical High-Risk.Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Feb 13;13:47. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00047. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30814943 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: Implications for Reward Processing and Motivational Deficits.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 20;11:46. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00046. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32153436 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crow TJ. Positive and negative schizophrenia symptoms and the role of dopamine. Br J Psychiatry. 1981;139:251–254. - PubMed
-
- Laruelle M, Kegeles LS, Abi-Dargham A. Glutamate, dopamine, and schizophrenia: from pathophysiology to treatment. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003;1003:138–158. - PubMed
-
- Angrist B, Sathananthan G, Wilk S, Gershon S. Amphetamine psychosis: behavioral and biochemical aspects. J Psychiatr Res. 1974;11:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Krystal JH, Perry EB, Jr, Gueorguieva R, Belger A, Madonick SH, Abi-Dargham A, et al. Comparative and interactive human psychopharmacologic effects of ketamine and amphetamine: implications for glutamatergic and dopaminergic model psychoses and cognitive function. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2005;62:985–994. - PubMed

