A new classification system for the actions of IRS chemicals traditionally used for malaria control
- PMID: 17684562
- PMCID: PMC1934935
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000716
A new classification system for the actions of IRS chemicals traditionally used for malaria control
Abstract
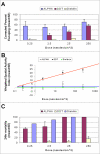
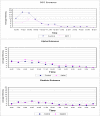
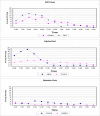
Knowledge of how mosquitoes respond to insecticides is of paramount importance in understanding how an insecticide functions to prevent disease transmission. A suite of laboratory assays was used to quantitatively characterize mosquito responses to toxic, contact irritant, and non-contact spatial repellent actions of standard insecticides. Highly replicated tests of these compounds over a range of concentrations proved that all were toxic, some were contact irritants, and even fewer were non-contact repellents. Of many chemicals tested, three were selected for testing in experimental huts to confirm that chemical actions documented in laboratory tests are also expressed in the field. The laboratory tests showed the primary action of DDT is repellent, alphacypermethrin is irritant, and dieldrin is only toxic. These tests were followed with hut studies in Thailand against marked-released populations. DDT exhibited a highly protective level of repellency that kept mosquitoes outside of huts. Alphacypermethrin did not keep mosquitoes out, but its strong irritant action caused them to prematurely exit the treated house. Dieldrin was highly toxic but showed no irritant or repellent action. Based on the combination of laboratory and confirmatory field data, we propose a new paradigm for classifying chemicals used for vector control according to how the chemicals actually function to prevent disease transmission inside houses. The new classification scheme will characterize chemicals on the basis of spatial repellent, contact irritant and toxic actions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kennedy JS. The excitant and repellent effects on mosquitoes of sublethal contacts with DDT. Bull Entomol Res. 1947;37:593–607. - PubMed
-
- Dethier VG, Browne LB, Smith CN. The designation of chemicals in terms of the responses they elicit for insects. J Econ Ent. 1960;53:134–136.
-
- Muirhead-Thomson RC. London: Edward Arnold and Company; 1953. Mosquito behavior in relation to malaria transmission and control in the tropics. p. 219.
-
- WHO [World Health Organization] 2006. Malaria vector control and personal protection. WHO technical report series no 936. - PubMed
-
- Shreck CE, McGovern TP. Repellents and other personal protection strategies against Aedes albopictus. J Am. Mosq Control Assoc. 1989;5:247–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

