Primary spinal intradural extramedullary hydatid cyst in a child
- PMID: 17684899
- PMCID: PMC2031965
Primary spinal intradural extramedullary hydatid cyst in a child
Abstract
Background/objective: Spinal hydatid cyst is a serious form of hydatid disease affecting less than 1% of the total cases of hydatid disease. We present a case of pathologically confirmed primary intradural spinal cyst hydatid in an otherwise healthy patient who showed no other evidence of systemic hydatid cyst disease.
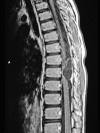
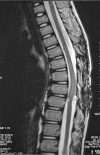
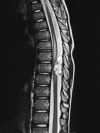
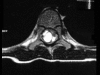
Case report: An 8-year-old boy presented with back pain, left leg pain, and difficulty in walking. The patient had no other signs of systemic hydatid cyst disease. An intradural extramedullary cystic lesion was identified with magnetic resonance imaging and was shown to be a hydatid cyst by histopathologic examination after the surgical removal.
Conclusion: Although extremely rare, primary intradural extramedullary hydatid cyst pathology might be the cause of leg pain and gait disturbance in children living in endemic areas.
Figures

References
-
- Pamir MN, Akalan N, Özgen T, et al. Spinal hydatid cyst. Surg Neurol. 1984. pp. 53–57. - PubMed
-
- Schnepper G, Johnson WD. Recurrent spinal hydatidosis in North America. Case report and review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus. 2004;17:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Kahilog ullarl G, Tuna H, Aydln Z, et al. Primary intradural extramedullary hydatid cyst. Am J Med Sci. 2005;329:202–204. - PubMed
-
- Pandey M, Chadudhari MP. Primary hydatid cysts of sacral spinal canal: case report. Neurosurgery. 1997;40:407–409. - PubMed
-
- Fahl M, Haddad FS, Huballah M, et al. Magnetic resonance imagining in intradural and extradural spinal echinococco-sis. Clin Imaging. 1994;18:179–183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
