Effects of simulated altitude (normobaric hypoxia) on cardiorespiratory parameters and circulating endothelial precursors in healthy subjects
- PMID: 17686146
- PMCID: PMC1976104
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-8-58
Effects of simulated altitude (normobaric hypoxia) on cardiorespiratory parameters and circulating endothelial precursors in healthy subjects
Abstract
Background: Circulating Endothelial Precursors (PB-EPCs) are involved in the maintenance of the endothelial compartment being promptly mobilized after injuries of the vascular endothelium, but the effects of a brief normobaric hypoxia on PB-EPCs in healthy subjects are scarcely studied.
Methods: Clinical and molecular parameters were investigated in healthy subjects (n = 8) in basal conditions (T0) and after 1 h of normobaric hypoxia (T1), with Inspiratory Fraction of Oxygen set at 11.2% simulating 4850 mt of altitude. Blood samples were obtained at T0 and T1, as well as 7 days after hypoxia (T2).
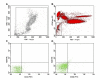
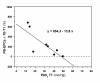
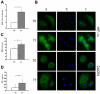
Results: In all studied subjects we observed a prompt and significant increase in PB-EPCs, with a return to basal value at T2. The induction of hypoxia was confirmed by Alveolar Oxygen Partial Pressure (PAO2) and Spot Oxygen Saturation decreases. Heart rate increased, but arterial pressure and respiratory response were unaffected. The change in PB-EPCs percent from T0 to T1 was inversely related to PAO2 at T1. Rapid (T1) increases in serum levels of hepatocyte growth factor and erythropoietin, as well as in cellular PB-EPCs-expression of Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha were observed.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the endothelial compartment seems quite responsive to standardized brief hypoxia, possibly important for PB-EPCs activation and recruitment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decrease in circulating plasmacytoid dendritic cells during short-term systemic normobaric hypoxia.Eur J Clin Invest. 2016 Feb;46(2):115-22. doi: 10.1111/eci.12416. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Eur J Clin Invest. 2016. PMID: 25652640
-
Acute ventilatory response to simulated altitude, normobaric hypoxia, and hypobaria.Aviat Space Environ Med. 1996 Nov;67(11):1019-22. Aviat Space Environ Med. 1996. PMID: 8908337
-
Effects of hypobaric hypoxia on vascular endothelial growth factor and the acute phase response in subjects who are susceptible to high-altitude pulmonary oedema.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000 Apr;81(6):497-503. doi: 10.1007/s004210050074. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10774874
-
Lower exhaled nitric oxide in hypobaric than in normobaric acute hypoxia.Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009 Oct 31;169(1):74-7. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2009.08.006. Epub 2009 Aug 15. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19686871
-
The Effect of Normobaric Hypoxia in Middle- and/or Long-Distance Runners: Systematic Review.Biology (Basel). 2022 Apr 30;11(5):689. doi: 10.3390/biology11050689. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fast reduction of peripheral blood endothelial progenitor cells in healthy humans exposed to acute systemic hypoxia.J Physiol. 2012 Feb 1;590(3):519-32. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.223032. Epub 2011 Dec 12. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22155931 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Can hypoxic exercise retard cellular senescence? A narrative review.Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2024 Nov 13;21(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s11556-024-00352-9. Eur Rev Aging Phys Act. 2024. PMID: 39533169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sleep Apnea Indices Associated with Markers of Inflammation and Cardiovascular Disease: A Proteomic Study in the MUSTACHE Cohort.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2024 Jan;21(1):165-169. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202305-472RL. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2024. PMID: 37788298 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Acute Exercise in Hypobaric Hypoxia Attenuates Endothelial Shedding in Subjects Unacclimatized to High Altitudes.Front Physiol. 2020 Feb 4;10:1632. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01632. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32116736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asahara T, Masuda H, Takahashi T, Kalka C, Pastore C, Silver M, Kearne M, Magner M, Isner JM. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization. Circ Res. 1999;85:221–228. - PubMed
-
- Ciulla MM, Lazzari L, Pacchiana R, Esposito A, Bosari S, Ferrero S, Gianelli U, Paliotti R, Busca G, Giorgetti A, Magrini F, Rebulla P. Homing of peripherally injected bone marrow cells in rat after experimental myocardial injury. Haematologica. 2003;88:614–621. - PubMed
-
- Crosby JR, Kaminski WE, Schatteman G, Martin PJ, Raines EW, Seifert RA, Bowen-Pope DF. Endothelial cells of hematopoietic origin make a significant contribution to adult blood vessel formation. Circ Res. 2000;87:728–730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

