Adjuvant trastuzumab in the treatment of her-2-positive early breast cancer: a meta-analysis of published randomized trials
- PMID: 17686164
- PMCID: PMC1959236
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-153
Adjuvant trastuzumab in the treatment of her-2-positive early breast cancer: a meta-analysis of published randomized trials
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women in the U.S. and Western Europe. Amplification of the her-2/neu gene occurs in approximately 25% of invasive ductal carcinomas of the breast. The first HER-2/neu-targeted approach to reach the clinic was trastuzumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against the extracellular domain of the HER-2/neu protein. Trastuzumab therapy prolongs the survival of patients with metastático HER-2/neu-overexpressing breast cancer when combined with chemotherapy and has recently been demonstrated to lead to dramatic improvements in disease-free survival when used in the adjuvant therapy setting in combination with or following chemotherapy. Here, we performed a meta-analysis of completed clinical trials of adjuvant trastuzumab in the adjuvant setting. Survival, recurrence, brain metastases, cardiotoxicity and directions for future research are discussed.
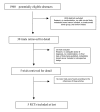
Methods: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCT) was performed comparing adjuvant trastuzumab treatment for HER2-positive early breast cancer (EBC) to observation. The MEDLINE, EMBASE, CANCERLIT and Cochrane Library databases, and abstracts published in the annual proceedings were systematically searched for evidence. Relevant reports were reviewed by two reviewers independently and the references from these reports were searched for additional trials, using guidelines set by QUOROM statement criteria.
Results: Pooled results from that five randomized trials of adjuvant Trastuzumab showed a significant reduction of mortality (p < 0.00001), recurrence (p < 0.00001), metastases rates (p < 0.00001) and second tumors other than breast cancer (p = 0.007) as compared to no adjuvant Trastuzumab patients. There were more grade III or IV cardiac toxicity after trastuzumab (203/4555 = 4.5%) versus no trastuzumab (86/4562 = 1.8%). The likelihood of cardiac toxicity was 2.45-fold higher (95% CI 1.89 - 3.16) in trastuzumab arms, however that result was associated with heterogeneity. The likelihood of brain metastases was 1.82-fold higher (95% CI 1.16 - 2.85) in patients who received trastuzumab.
Conclusion: The results from this meta-analysis are sufficiently compelling to consider 1 year of adjuvant trastuzumab treatment for women with HER-2-positive EBC based on the risk: benefit ratio demonstrated in these studies. Adequate assessment of HER-2/neu status is critical, and careful cardiac monitoring is warranted because of cardiac toxicity. Clinical trials should be designed to answer unsolved questions.
Figures






References
-
- Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:10–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

