Semi-allogeneic vaccine for T-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 17686178
- PMCID: PMC1971246
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-5-39
Semi-allogeneic vaccine for T-cell lymphoma
Abstract
Background: Experimental results from studies with inbred mice and their syngeneic tumors indicated that the inoculation of semi-allogeneic cell hybrids (derived from the fusion between syngeneic tumor cells and an allogeneic cell line) protects the animal host from a subsequent lethal challenge with unmodified syngeneic tumor cells.
Methods: Semi-allogeneic somatic cell hybrids were generated by the fusion of EL-4 T lymphoma cells (H-2b) and BALB/c-derived renal adenocarcinoma RAG cells (H-2d). Cell hybrids were injected intra-peritoneally (i.p.) in C57BL/6 mice (H-2b) before challenging the mice with a tumorigenic dose of EL-4 cells.
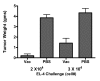
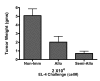
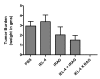
Results: Semi-allogeneic tumor cell hybrids could not form a tumor in the animal host because they expressed allogeneic determinants (H-2d) and were rejected as a transplant. However, they conferred protection against a tumorigenic challenge of EL-4 cells compared to control mice that were mock-vaccinated with i.p.-injected phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and in which EL-4 lymphomas grew rapidly to a large size in the peritoneal cavity. Screening of spleen-derived RNA by means of focused microarray technology revealed up-regulation of genes involved in the Th-1-type immune response and in the activation of dendritic antigen-presenting cells (APC).
Conclusion: The results of our studies are entirely consistent with the concept that CD80- and CD86-expressing APC play a central role in mediating the immune protection induced by semi-allogeneic vaccines by activating a Th-1 response and instructing T cells responsible for killing autologous tumor cells.
Figures
References
-
- Jami J, Ritz E. Expression of tumor-specific antigens in mouse somatic cell hybrids. Cancer Res. 1973;33:2524–2528. - PubMed
-
- Parkman R. Tumor hybrid cells: an immunotherapeutic agent. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974;52:1541–1545. - PubMed
-
- Kim BS. Tumor-specific immunity induced by somatic hybrids. II. Elicitation of enhanced immunity against the parent plasmacytoma. J Immunol. 1979;123:739–744. - PubMed
-
- Kim BS, Liang W, Cohen EP. Tumor-specific immunity induced by somatic hybrids. I. Lack of relationship between immunogenicity and tumorigenicity of selected hybrids. J Immunol. 1979;123:733–738. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

