PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants
- PMID: 17686513
- PMCID: PMC2040108
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.07.013
PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants
Abstract
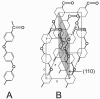
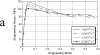
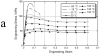
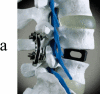
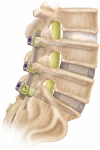
Since the 1980s, polyaryletherketones (PAEKs) have been increasingly employed as biomaterials for trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. We have synthesized the extensive polymer science literature as it relates to structure, mechanical properties, and chemical resistance of PAEK biomaterials. With this foundation, one can more readily appreciate why this family of polymers will be inherently strong, inert, and biocompatible. Due to its relative inertness, PEEK biomaterials are an attractive platform upon which to develop novel bioactive materials, and some steps have already been taken in that direction, with the blending of HA and TCP into sintered PEEK. However, to date, blended HA-PEEK composites have involved a trade-off in mechanical properties in exchange for their increased bioactivity. PEEK has had the greatest clinical impact in the field of spine implant design, and PEEK is now broadly accepted as a radiolucent alternative to metallic biomaterials in the spine community. For mature fields, such as total joint replacements and fracture fixation implants, radiolucency is an attractive but not necessarily critical material feature.
Figures
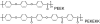




References
-
- Williams DF, McNamara A, Turner RM. Potential of polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and carbon-fibre-reinforced PEEK in medical applications. J Mat Sci Letters. 1987;6:199–190.
-
- May R. Polyetheretherketones. In: Mark HF, Bikales NM, Overberger CG, Menges G, Kroschiwitz JI, editors. Encyclopedia of Polymer Science and Engineering. John Wiley and Sons; New York: 1988. pp. 313–320.
-
- Rigby RB. Polyetheretherketone. In: Margolis JM, editor. Engineering Thermoplastics: Properties and Applications. Marcel Dekker, Inc.; New York: 1985. pp. 299–314.
-
- Skinner HB. Composite technology for total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988 Oct;(235):224–236. - PubMed
-
- Brown SA, Hastings RS, Mason JJ, Moet A. Characterization of short-fibre reinforced thermoplastics for fracture fixation devices. Biomaterials. 1990;11(8):541–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

