Antisense transcription in the human cytomegalovirus transcriptome
- PMID: 17686857
- PMCID: PMC2045512
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00007-07
Antisense transcription in the human cytomegalovirus transcriptome
Abstract
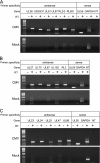
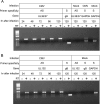
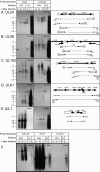
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infections are prevalent in human populations and can cause serious diseases, especially in those with compromised or immature immune systems. The HCMV genome of 230 kb is among the largest of the herpesvirus genomes. Although the entire sequence of the laboratory-adapted AD169 strain of HCMV has been available for 18 years, the precise number of viral genes is still in question. We undertook an analysis of the HCMV transcriptome as an approach to enumerate and analyze the gene products of HCMV. Transcripts of HCMV-infected fibroblasts were isolated at different times after infection and used to generate cDNA libraries representing different temporal classes of viral genes. cDNA clones harboring viral sequences were selected and subjected to sequence analysis. Of the 604 clones analyzed, 45% were derived from genomic regions predicted to be noncoding. Additionally, at least 55% of the cDNA clones in this study were completely or partially antisense to known or predicted HCMV genes. The remarkable accumulation of antisense transcripts during infection suggests that currently available genomic maps based on open-reading-frame and other in silico analyses may drastically underestimate the true complexity of viral gene products. These findings also raise the possibility that aspects of both the HCMV life cycle and genome organization are influenced by antisense transcription. Correspondingly, virus-derived noncoding and antisense transcripts may shed light on HCMV pathogenesis and may represent a new class of targets for antiviral therapies.
Figures
References
-
- Bankier, A. T., S. Beck, R. Bohni, C. M. Brown, R. Cerny, M. S. Chee, C. A. Hutchison III, T. Kouzarides, J. A. Martignetti, E. Preddie, et al. 1991. The DNA sequence of the human cytomegalovirus genome. DNA Seq. 2:1-12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

