Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in immature and mature dendritic cells reveals dissociable cis- and trans-infection
- PMID: 17686876
- PMCID: PMC2045571
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01081-07
Characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in immature and mature dendritic cells reveals dissociable cis- and trans-infection
Abstract
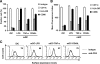
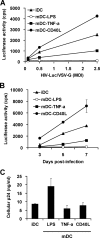
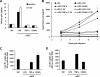
Dendritic cells (DCs) transmit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) to CD4(+) T cells through the trans- and cis-infection pathways; however, little is known about the relative efficiencies of these pathways and whether they are interdependent. Here we compare cis- and trans-infections of HIV-1 mediated by immature DCs (iDCs) and mature DCs (mDCs), using replication-competent and single-cycle HIV-1. Monocyte-derived iDCs were differentiated into various types of mDCs by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), and CD40 ligand (CD40L). iDCs and CD40L-induced mDCs were susceptible to HIV-1 infection and mediated efficient viral transmission to CD4(+) T cells. Although HIV-1 cis-infection was partially restricted in TNF-alpha-induced mDCs and profoundly blocked in LPS-induced mDCs, these cells efficiently promoted HIV-1 trans-infection of CD4(+) T cells. The postentry restriction of HIV-1 infection in LPS-induced mDCs was identified at the levels of reverse transcription and postintegration, using real-time PCR quantification of viral DNA and integration. Furthermore, nucleofection of DCs with HIV-1 proviral DNA confirmed that impaired gene expression of LPS-induced mDCs was responsible for the postentry restriction of HIV-1 infection. Our results suggest that various DC subsets in vivo may differentially contribute to HIV-1 dissemination via dissociable cis- and trans-infections.
Figures




References
-
- Ardeshna, K. M., A. R. Pizzey, S. Devereux, and A. Khwaja. 2000. The PI3 kinase, p38 SAP kinase, and NF-kappaB signal transduction pathways are involved in the survival and maturation of lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Blood 96:1039-1046. - PubMed
-
- Bakri, Y., C. Schiffer, V. Zennou, P. Charneau, E. Kahn, A. Benjouad, J. C. Gluckman, and B. Canque. 2001. The maturation of dendritic cells results in postintegration inhibition of HIV-1 replication. J. Immunol. 166:3780-3788. - PubMed
-
- Banchereau, J., and R. M. Steinman. 1998. Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392:245-252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

