Evidence of increased inflammation and microcirculatory abnormalities in patients with type 1 diabetes and their role in microvascular complications
- PMID: 17686944
- PMCID: PMC2692935
- DOI: 10.2337/db07-0784
Evidence of increased inflammation and microcirculatory abnormalities in patients with type 1 diabetes and their role in microvascular complications
Abstract
Objective: Type 1 diabetes is associated with increased microvascular complications and inflammation. The monocyte-macrophage is a pivotal cell in atherogenesis. There are scanty data on noninvasive measures of microvascular abnormalities and inflammation in type 1 diabetic subjects with microvascular complications. Thus, we examined systemic and cellular biomarkers of inflammation in type 1 diabetic patients with microvascular complications (T1DM-MV patients) and type 1 diabetic patients without microvascular complications (T1DM patients) compared with matched control subjects and determined the microcirculatory abnormalities in the T1DM and T1DM-MV patients using computer-assisted intravital microscopy (CAIM).
Research design and methods: Fasting blood, 24-h urine, and CAIM measurements were obtained from the T1DM and T1DM-MV patients and matched control subjects. C-reactive protein, E-selectin, nitrotyrosine, monocyte superoxide, and cytokines were elevated in the T1DM and T1DM-MV patients compared with control subjects (P < 0.01).
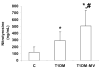
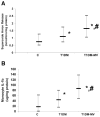
Results: Severity index, as assessed by CAIM, was significantly increased in the T1DM and T1DM-MV patients compared with the control subjects (P < 0.001). There was a significant increase in C-reactive protein, nitrotyrosine, vascular cell adhesion molecule and monocyte superoxide anion release, and interleukin-1 release in T1DM-MV compared with T1DM patients (P < 0.05). T1DM-MV patients had significantly increased CAIM severity index and microalbumin-to-creatinine ratio compared with T1DM patients (P < 0.05). Furthermore, pp38MAPK, pp65, and pERK activity were significantly increased in monocytes from the T1DM and T1DM-MV patients compared with those from the controls subjects, and pp38MAPK and pp65 activity were significantly increased in the T1DM-MV compared with the T1DM patients (P < 0.01).
Conclusions: T1DM-MV patients have increased inflammation compared with T1DM patients. CAIM provides an effective biomarker of microvascular complications, since it is significantly elevated in T1DM-MV compared with T1DM patients and can be monitored following therapies targeted at improving inflammation and/or microvascular complications of type 1 diabetes.
Figures

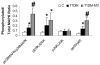
References
-
- Libby P, Nathan DM, Abraham K, Brunzell JD, Fradkin JE, Haffner SM, Hsueh W, Rewers M, Roberts BT, Savage PJ, Skarlatos S, Wassef M, Rabadan-Diehl C. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Working Group on Cardiovascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Report of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute–National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Working Group on Cardiovascular Complications of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Circulation. 2005;111:3489–3493. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–874. - PubMed
-
- Devaraj S, Jialal I. Low-density lipoprotein postsecretory modification, monocyte function, and circulating adhesion molecules in type 2 diabetic patients with and without macrovascular complications: the effect of alpha-tocopherol supplementation. Circulation. 2000;102:191–196. - PubMed
-
- Devaraj S, Jialal I. Alpha tocopherol supplementation decreases serum C-reactive protein and monocyte interleukin-6 levels in normal volunteers and type 2 diabetic patients. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;29:790–792. - PubMed
-
- Cipolletta C, Ryan KE, Hanna EV, Trimble ER. Activation of peripheral blood CD14+ monocytes occurs in diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54:2779–2786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

