DNA repair capacity of zebrafish
- PMID: 17686971
- PMCID: PMC1948947
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0706157104
DNA repair capacity of zebrafish
Abstract
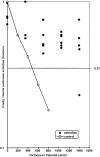
Damage to the genome is unavoidable in living creatures, because of sunlight exposure as well as environmental chemicals present in food and drinking water. There is a need to monitor and purify the drinking water; therefore, several methods of detection have been developed. A very promising model system for this purpose is the zebrafish (Danio rerio), which is endowed with special qualities for detecting external as well as internal abnormalities. Grossman and Wei's assay [Grossman L, Wei Q (1995) Clin Chem 12:1854-1863], which measures the expression level of a nonreplicating recombinant plasmid DNA containing a UV-damaged luciferase reporter gene, shows that zebrafish can repair chromosomal lesions to a much greater extent than the human population. This vertebrate model is still very promising after possible down-regulation of the DNA repair enzymes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mizell M, Romig ES. Int J Dev Biol. 1997;41:411–423. - PubMed
-
- Carvan MJ, III, Sonntag DM, Cmar CB, Cook RS, Curran MA, Miller GL. Sci Total Environ. 2001;274:183–196. - PubMed
-
- Ames BN, Mccann J, Yamasaki E. Mutat Res. 1975;31:347–364. - PubMed
-
- Amatruda JF, Shepard JL, Stern HM, Zon LI. Mutat Res. 1975;31:347–364.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources