Exocyst requirement for endocytic traffic directed toward the apical and basolateral poles of polarized MDCK cells
- PMID: 17686995
- PMCID: PMC1995710
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e07-02-0097
Exocyst requirement for endocytic traffic directed toward the apical and basolateral poles of polarized MDCK cells
Abstract
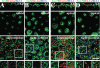
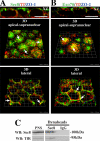
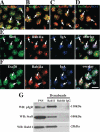
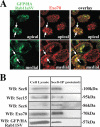
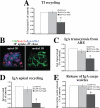
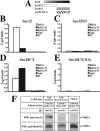
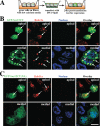
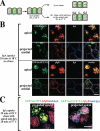
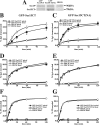
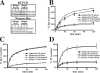
The octameric exocyst complex is associated with the junctional complex and recycling endosomes and is proposed to selectively tether cargo vesicles directed toward the basolateral surface of polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells. We observed that the exocyst subunits Sec6, Sec8, and Exo70 were localized to early endosomes, transferrin-positive common recycling endosomes, and Rab11a-positive apical recycling endosomes of polarized MDCK cells. Consistent with its localization to multiple populations of endosomes, addition of function-blocking Sec8 antibodies to streptolysin-O-permeabilized cells revealed exocyst requirements for several endocytic pathways including basolateral recycling, apical recycling, and basolateral-to-apical transcytosis. The latter was selectively dependent on interactions between the small GTPase Rab11a and Sec15A and was inhibited by expression of the C-terminus of Sec15A or down-regulation of Sec15A expression using shRNA. These results indicate that the exocyst complex may be a multipurpose regulator of endocytic traffic directed toward both poles of polarized epithelial cells and that transcytotic traffic is likely to require Rab11a-dependent recruitment and modulation of exocyst function, likely through interactions with Sec15A.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK048370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054425/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-54425/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-54407/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-070856/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK043405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS0-38892/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 DK043405/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK054425/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS038892/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054407/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-48370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM067002/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK051970/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- GM-67002/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK-43405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK070856/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK070856/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-51970/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

