Identification of less-common Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes by a multiplex PCR-based reverse line blot hybridization assay
- PMID: 17687009
- PMCID: PMC2045372
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01076-07
Identification of less-common Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes by a multiplex PCR-based reverse line blot hybridization assay
Abstract
We developed a multiplex PCR-based reverse line blot (mPCR/RLB) assay to identify 50 uncommon pneumococcal serotypes. In combination with a previously described mPCR/RLB assay (3), all 90 pneumococcal serotypes can be identified individually (32 serotypes) or, because of predictable cross-reactions, to within small groups of two to five related serotypes (58 serotypes), which can be distinguished using serotype-specific antisera.
Figures
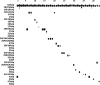
References
-
- Bentley, S. D., D. M. Aanensen, A. Mavroidi, D. Saunders, E. Rabbinowitsch, M. Collins, K. Donohoe, D. Harris, L. Murphy, M. A. Quail, G. Samuel, I. C. Skovsted, M. S. Kaltoft, B. Barrell, P. R. Reeves, J. Parkhill, and B. G. Spratt. 2006. Genetic analysis of the capsular biosynthetic locus from all 90 pneumococcal serotypes. PLoS Genet. 2:e31. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kong, F., and G. L. Gilbert. 2003. Using cpsA-cpsB sequence polymorphisms and serotype-/group-specific PCR to predict 51 Streptococcus pneumoniae capsular serotypes. J. Med. Microbiol. 52:1047-1058. - PubMed
-
- Kong, F., and G. L. Gilbert. 2006. Multiplex PCR-based reverse line blot hybridization assay (mPCR/RLB)—a practical epidemiological and diagnostic tool. Nat. Protoc. 1:2668-2680. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

