Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana, three new Sporothrix species of clinical interest
- PMID: 17687013
- PMCID: PMC2045377
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00808-07
Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana, three new Sporothrix species of clinical interest
Abstract
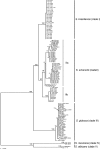
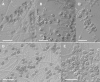
Sporothrix schenckii is the species responsible for sporotrichosis, a fungal infection caused by the traumatic implantation of this dimorphic fungus. Recent molecular studies have demonstrated that this species constitutes a complex of numerous phylogenetic species. Since the delineation of such species could be of extreme importance from a clinical point of view, we have studied a total of 127 isolates, most of which were received as S. schenckii, including the available type strains of species currently considered synonyms, and also some close morphological species. We have phenotypically characterized all these isolates using different culture media, growth rates at different temperatures, and numerous nutritional tests and compared their calmodulin gene sequences. The molecular analysis revealed that Sporothrix albicans, S. inflata, and S. schenckii var. luriei are species that are clearly different from S. schenckii. The combination of these phenetic and genetic approaches allowed us to propose the new species Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana. The key phenotypic features for recognizing these species are the morphology of the sessile pigmented conidia, growth at 30, 35, and 37 degrees C, and the assimilation of sucrose, raffinose, and ribitol.
Figures
References
-
- Beard, C. B., J. L. Carter, S. P. Keely, L. Huang, N. J. Pieniazek, I. N. Moura, J. M. Roberts, A. W. Hightower, M. S. Bens, A. R. Freeman, S. Lee, J. R. Stringer, J. S. Duchin, C. del Rio, D. Rimland, R. P. Baughman, D. A. Levy, V. J. Dietz, P. Simon, and T. R. Navin. 2000. Genetic variation in Pneumocystis carinii isolates from different geographic regions: implications for transmission. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 6:265-272. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berbee, M. L., and J. W. Taylor. 1992. 18S ribosomal RNA gene sequence characters place the human pathogen Sporothrix schenckii in the genus Ophiostoma. Exp. Mycol. 16:87-91.
-
- da Rosa, A. C., M. L. Scroferneker, R. Vettorato, R. L. Gervini, G. Vettorato, and A. Weber. 2005. Epidemiology of sporotrichosis: a study of 304 cases in Brazil. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 52:451-459. - PubMed
-
- de Beer, Z. W., T. C. Harrington, H. F. Vismer, B. D. Wingfield, and M. J. Wingfield. 2003. Phylogeny of the Ophiostoma stenoceras-Sporothrix schenckii complex. Mycologia 95:434-441. - PubMed
-
- de Hoog, G. S. 1974. The genera Blastobotrys, Sporothrix, Calcarisporium and Calcarisporiella gen. nov. Stud. Mycol. 7:1-84.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

