Competing interactions between micro-RNAs determine neural progenitor survival and proliferation after ethanol exposure: evidence from an ex vivo model of the fetal cerebral cortical neuroepithelium
- PMID: 17687032
- PMCID: PMC2915840
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1269-07.2007
Competing interactions between micro-RNAs determine neural progenitor survival and proliferation after ethanol exposure: evidence from an ex vivo model of the fetal cerebral cortical neuroepithelium
Abstract
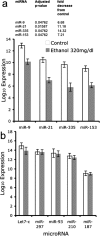
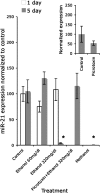
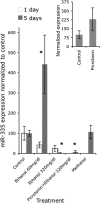
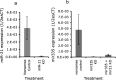
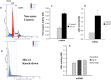
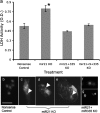
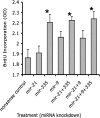
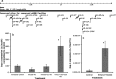
The fetal brain is sensitive to a variety of teratogens, including ethanol. We showed previously that ethanol induced mitosis and stem cell maturation, but not death, in fetal cerebral cortex-derived progenitors. We tested the hypothesis that micro-RNAs (miRNAs) could mediate the teratogenic effects of ethanol in a fetal mouse cerebral cortex-derived neurosphere culture model. Ethanol, at a level attained by alcoholics, significantly suppressed the expression of four miRNAs, miR-21, -335, -9, and -153, whereas a lower ethanol concentration, attainable during social drinking, induced miR-335 expression. A GABA(A) receptor-dependent mechanism mediated miR-21, but not miR-335 suppression, suggesting that divergent mechanisms regulate ethanol-sensitive miRNAs. Antisense-mediated suppression of miR-21 expression resulted in apoptosis, suggesting that miR-21 is an antiapoptotic factor. miR-335 knockdown promoted cell proliferation and prevented death induced by concurrently suppressing miR-21, indicating that miR-335 is a proapoptotic, antimitogenic factor whose actions are antagonistic to miR-21. Computational analyses identified two genes, Jagged-1, a Notch-receptor ligand, and embryonic-lethal abnormal vision, Drosophila-like 2 (ELAVL2), a brain-specific regulator of RNA stability, as presumptive targets of three of four ethanol-sensitive micro-RNAs. Combined knockdown of miR-335, -21, and -153 significantly increased Jagged-1 mRNA. Furthermore, ethanol induced both Jagged-1 and ELAVL2 mRNA. The collective suppression of micro-RNAs is consistent with ethanol induction of cell cycle and neuroepithelial maturation in the absence of apoptosis. These data identify a role for micro-RNAs as epigenetic intermediaries, which permit teratogens to shape complex, divergent developmental processes, and additionally demonstrate that coordinately regulated miRNAs exhibit both functional synergy and antagonism toward each other.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ethanol exposure during neurogenesis induces persistent effects on neural maturation: evidence from an ex vivo model of fetal cerebral cortical neuroepithelial progenitor maturation.Gene Expr. 2008;14(3):159-71. Gene Expr. 2008. PMID: 18590052 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing actions of ethanol and nicotine on microRNAs are mediated by nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in fetal cerebral cortical-derived neural progenitor cells.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012 Oct;36(10):1669-77. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2012.01793.x. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012. PMID: 22458409 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol induces cell-cycle activity and reduces stem cell diversity to alter both regenerative capacity and differentiation potential of cerebral cortical neuroepithelial precursors.BMC Neurosci. 2005 Sep 13;6:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-6-59. BMC Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16159388 Free PMC article.
-
The cell biology of neural stem and progenitor cells and its significance for their proliferation versus differentiation during mammalian brain development.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;20(6):707-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.09.008. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18930817 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: master regulators of ethanol abuse and toxicity?Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010 Apr;34(4):575-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2009.01126.x. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2010. PMID: 20102566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CD24 induces expression of the oncomir miR-21 via Src, and CD24 and Src are both post-transcriptionally downregulated by the tumor suppressor miR-34a.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059563. Epub 2013 Mar 22. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23533633 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol Exposure Increases miR-140 in Extracellular Vesicles: Implications for Fetal Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Maturation.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019 Jul;43(7):1414-1426. doi: 10.1111/acer.14066. Epub 2019 May 14. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2019. PMID: 31009095 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in the pathophysiology and treatment of status epilepticus.Front Mol Neurosci. 2013 Nov 12;6:37. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2013.00037. eCollection 2013. Front Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24282394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-335 orchestrates cell proliferation, migration and differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Jun;18(6):985-95. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2010.167. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21164520 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-153 targets the nuclear factor-1 family and protects against teratogenic effects of ethanol exposure in fetal neural stem cells.Biol Open. 2014 Jul 25;3(8):741-58. doi: 10.1242/bio.20147765. Biol Open. 2014. PMID: 25063196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe K, Niikura Y, Misawa M. GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition by ethanol of long-term potentiation in the basolateral amygdala-dentate gyrus pathway in vivo. Neuroscience. 2004;125:113–117. - PubMed
-
- Abrahante JE, Daul AL, Li M, Volk ML, Tennessen JM, Miller EA, Rougvie AE. The Caenorhabditis elegans hunchback-like gene lin-57/hbl-1 controls developmental time and is regulated by microRNAs. Dev Cell. 2003;4:625–637. - PubMed
-
- Adachi J, Mizoi Y, Fukunaga T, Ogawa Y, Ueno Y, Imamichi H. Degrees of alcohol intoxication in 117 hospitalized cases. J Stud Alcohol. 1991;52:448–453. - PubMed
-
- Akamatsu W, Okano HJ, Osumi N, Inoue T, Nakamura S, Sakakibara S, Miura M, Matsuo N, Darnell RB, Okano H. Mammalian ELAV-like neuronal RNA-binding proteins HuB and HuC promote neuronal development in both the central and the peripheral nervous systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96:9885–9890. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
