Functional properties of neurons derived from in vitro reprogrammed postnatal astroglia
- PMID: 17687043
- PMCID: PMC6672931
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1615-07.2007
Functional properties of neurons derived from in vitro reprogrammed postnatal astroglia
Abstract
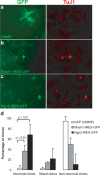
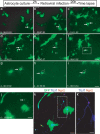
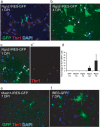
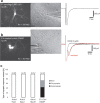
With the exception of astroglia-like cells in the neurogenic niches of the telencephalic subependymal or hippocampal subgranular zone, astroglia in all other regions of the adult mouse brain do not normally generate neurons. Previous studies have shown, however, that early postnatal cortical astroglia in culture can be reprogrammed to adopt a neuronal fate after forced expression of Pax6, a transcription factor (TF) required for proper neuronal specification during embryonic corticogenesis. Here we show that also the proneural genes neurogenin-2 and Mash1 (mammalian achaete schute homolog 1) possess the ability to reprogram astroglial cells from early postnatal cerebral cortex. By means of time-lapse imaging of green fluorescent astroglia, we provide direct evidence that it is indeed cells with astroglial characteristics that give rise to neurons. Using patch-clamp recordings in culture, we show that astroglia-derived neurons acquire active conductances and are capable of firing action potentials, thus displaying hallmarks of true neurons. However, independent of the TF used for reprogramming, astroglia-derived neurons appear to mature more slowly compared with embryonic-born neurons and fail to generate a functional presynaptic output within the culturing period. However, when cocultured with embryonic cortical neurons, astroglia-derived neurons receive synaptic input, demonstrating that they are competent of establishing a functional postsynaptic compartment. Our data demonstrate that single TFs are capable of inducing a remarkable functional reprogramming of astroglia toward a truly neuronal identity.
Figures





References
-
- Anderson S, Mione M, Yun K, Rubenstein JLR. Differential origins of neocortical projection and local circuit neurons: role of Dlx genes in neocortical interneuronogenesis. Cereb Cortex. 1999;9:646–654. - PubMed
-
- Bachoo RM, Maher EA, Ligon KL, Sharpless NE, Chan SS, You MJ, Tang Y, DeFrances J, Stover E, Weissleder R, Rowitch DH, Louis DN, DePinho RA. Convergent mechanisms governing terminal differentiation and transformation along the neural stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell. 2002;1:269–277. - PubMed
-
- Ballas N, Grunseich C, Lu DD, Speh JC, Mandel G. REST and its corepressors mediate plasticity of neuronal gene chromatin throughout neurogenesis. Cell. 2005;121:645–657. - PubMed
-
- Berninger B, Guillemot F, Götz M. Directing neurotransmitter identity of neurons derived from expanded adult neural stem cells. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25:2581–2590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
