The relationship between early childhood blood lead levels and performance on end-of-grade tests
- PMID: 17687454
- PMCID: PMC1940087
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.9994
The relationship between early childhood blood lead levels and performance on end-of-grade tests
Abstract
Background: Childhood lead poisoning remains a critical environmental health concern. Low-level lead exposure has been linked to decreased performance on standardized IQ tests for school-aged children.
Objective: In this study we sought to determine whether blood lead levels in early childhood are related to educational achievement in early elementary school as measured by performance on end-of-grade (EOG) testing.
Methods: Educational testing data for 4th-grade students from the 2000-2004 North Carolina Education Research Data Center were linked to blood lead surveillance data for seven counties in North Carolina and then analyzed using exploratory and multivariate statistical methods.
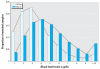
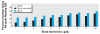
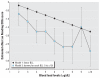
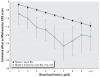
Results: The discernible impact of blood lead levels on EOG testing is demonstrated for early childhood blood lead levels as low as 2 microg/dL. A blood lead level of 5 microg/dL is associated with a decline in EOG reading (and mathematics) scores that is roughly equal to 15% (14%) of the interquartile range, and this impact is very significant in comparison with the effects of covariates typically considered profoundly influential on educational outcomes. Early childhood lead exposures appear to have more impact on performance on the reading than on the mathematics portions of the tests.
Conclusions: Our emphasis on population-level analyses of children who are roughly the same age linked to previous (rather than contemporaneous) blood lead levels using achievement (rather than aptitude) outcome complements the important work in this area by previous researchers. Our results suggest that the relationship between blood lead levels and cognitive outcomes are robust across outcome measures and at low levels of lead exposure.
Figures


Comment in
-
Guest editorial: Responding to blood lead levels < 10 microg/dL.Environ Health Perspect. 2008 Feb;116(2):A60-1. doi: 10.1289/ehp.10703. Environ Health Perspect. 2008. PMID: 18288294 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bacharach VR, Baumeister AA. Effects of maternal intelligence, marital status, income, and home environment on cognitive development of low birthweight infants. J Pediatr Psychol. 1998;23(3):197–205. - PubMed
-
- Bellinger DC, Stiles KM, Needleman HL. Low-level lead exposure, intelligence and academic achievement: a long-term follow-up study. Pediatrics. 1992;90(6):855–861. - PubMed
-
- CDC. Screening Young Children for Lead Poisoning: Guidance for State and Local Public Health Officials. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 1997.
-
- CDC. Laboratory Standardization: Lead. Atlanta, GA:Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2006. [[accessed 21 September 2006]]. Available: http://www.cdc.gov/nceh/dls/lead.htm.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
