Identification of a responsible promoter region and a key transcription factor, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein epsilon, for up-regulation of PHGPx in HL60 cells stimulated with TNF alpha
- PMID: 17688422
- PMCID: PMC2267347
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20070245
Identification of a responsible promoter region and a key transcription factor, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein epsilon, for up-regulation of PHGPx in HL60 cells stimulated with TNF alpha
Abstract
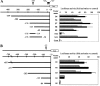
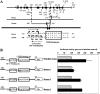
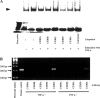
In the present study we investigated promoter regions of the PHGPx [phospholipid hydroperoxide GPx (glutathione peroxidase)] gene and transcription factors involved in TNFalpha (tumour necrosis factor alpha)-induced up-regulation of PHGPx in non-differentiated HL60 cells. Non-differentiated HL60 cells displayed up-regulation of non-mitochondrial and mitochondrial PHGPx mRNA in response to TNFalpha stimulation. The promoter activity was up-regulated by TNFalpha stimulation in cells transfected with a luciferase reporter vector encoding the region from -282 to -123 of the human PHGPx gene compared with the non-stimulated control. The up-regulated promoter activity was effectively abrogated by a mutation in the C/EBP (CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein)-binding sequence in this region. ChIP (chromatin immunoprecipitation) assays demonstrated that C/EBPepsilon bound to the -247 to -34 region in HL60 cells, but C/EBPalpha, beta, gamma and delta did not. The binding of C/EBPepsilon to the promoter region was increased in HL60 cells stimulated with TNFalpha compared with that of the non-stimulated control. An increased binding of nuclear protein to the C/EBP-binding sequence was observed by EMSA (electrophoretic mobility-shift assay) in cells stimulated with TNFalpha, and it was inhibited by pre-treatment with an anti-C/EBPepsilon antibody, but not with other antibodies. The C/EBPepsilon mRNA was expressed in PMNs (polymorphonuclear cells), non-differentiated HL60 cells and neutrophil-like differentiated HL60 cells displaying TNFalpha-induced up-regulation of PHGPx mRNA, but not in macrophage-like differentiated HL60 cells, HEK-293 cells (human embryonic kidney-293 cells) and other cell lines exhibiting no up-regulation. The up-regulation of PHGPx mRNA, however, was detected in HEK-293 cells overexpressing C/EBPepsilon as a result of TNFalpha stimulation. These results indicate that C/EBPepsilon is a critical transcription factor in TNFalpha-induced up-regulation of PHGPx expression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Induction of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils and HL60 cells stimulated with TNF-alpha.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Nov 18;337(2):464-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.09.076. Epub 2005 Sep 21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005. PMID: 16223606
-
Identification of the positive regulatory and distinct core regions of promoters, and transcriptional regulation in three types of mouse phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase.J Biochem. 2006 Oct;140(4):573-90. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvj186. Epub 2006 Sep 7. J Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16959796
-
The tumour necrosis factor-alpha-mediated suppression of the CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-alpha gene transcription in hepatocytes involves inhibition of autoregulation.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009 May;41(5):1189-97. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2008.10.024. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19027873
-
The role of C/EBP(epsilon) in the terminal stages of granulocyte differentiation.Stem Cells. 2001;19(2):125-33. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.19-2-125. Stem Cells. 2001. PMID: 11239167 Review.
-
[Molecular pathogenesis in tuberculosis complicated with AIDS].Kekkaku. 2004 Nov;79(11):659-67. Kekkaku. 2004. PMID: 15729891 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Edaravone ameliorates depressive and anxiety-like behaviors via Sirt1/Nrf2/HO-1/Gpx4 pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2022 Feb 7;19(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02400-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2022. PMID: 35130906 Free PMC article.
-
Basic biology and roles of CEBPD in cardiovascular disease.Cell Death Discov. 2025 Mar 14;11(1):102. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02357-4. Cell Death Discov. 2025. PMID: 40087290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventing oxidative stress: a new role for XBP1.Cell Death Differ. 2009 Jun;16(6):847-57. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2009.14. Epub 2009 Feb 27. Cell Death Differ. 2009. PMID: 19247368 Free PMC article.
-
New Strategy of Functional Analysis of PHGPx Knockout Mice Model Using Transgenic Rescue Method and Cre-LoxP System.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010 Jan;46(1):1-13. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.09-94R. Epub 2009 Dec 29. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20104259 Free PMC article.
-
PTGER3 knockdown inhibits the vulnerability of triple-negative breast cancer to ferroptosis.Cancer Sci. 2024 Jun;115(6):2067-2081. doi: 10.1111/cas.16169. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 38566528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Root R. K., Cohen M. S. The microbicidal mechanisms of human neutrophils and eosinophils. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1981;3:565–598. - PubMed
-
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1978;298:659–668. - PubMed
-
- Scapini P., Lapinet-Vera J. A., Gasperini S., Calzetti F., Bazzoni F., Cassatella M. A. The neutrophil as a cellular source of chemokines. Immunol. Rev. 2000;177:195–203. - PubMed
-
- Ford-Hutchinson A. W., Bray M. A., Doig M. V., Shipley M. E., Smith M. J. H. Leukotriene B, a potent chemokinetic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Nature. 1980;286:264–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

