Changes in beta 2-adrenoceptor and other signaling proteins produced by chronic administration of 'beta-blockers' in a murine asthma model
- PMID: 17689122
- PMCID: PMC2775056
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pupt.2007.06.003
Changes in beta 2-adrenoceptor and other signaling proteins produced by chronic administration of 'beta-blockers' in a murine asthma model
Abstract
Background: We have previously reported that chronic treatment with certain 'beta-blockers' reduces airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) to methacholine in a murine model of asthma.
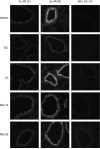
Methods: Airway resistance was measured using the forced oscillation technique in ovalbulmin-sensitized and ovalbulmin-challenged mice treated with several beta-adrenoceptor (beta-AR) ligands. We used the selective beta 2-AR ligand ICI 118,551 and the preferential beta 1-AR ligand metoprolol to investigate the receptor subtype mediating the beneficial effect. Expression of beta-ARs was evaluated using immunofluorescence. We evaluated several signaling proteins by western blot using lung homogenates, and measured the relaxation of the isolated trachea produced by EP2 and IP receptor agonists.
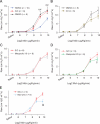
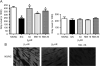
Results: Four findings were associated with the decreased AHR after chronic beta-blocker treatment: (1) the highly selective beta 2-AR antagonist/inverse agonist, ICI 118,551 produced the bronchoprotective effect; (2) beta 2-AR up-regulation resulted from chronic 'beta-blocker' treatment; (3) reduced expression of certain proteins involved in regulating bronchial tone, namely, Gi, phosphodiesterase 4D and phospholipase C-beta 1; and (4) an enhanced bronchodilatory response to prostanoid agonists for the IP and EP2 receptors.
Conclusions: These data suggest that in the murine model of asthma, several compensatory changes associated with either increased bronchodilator signaling or decreased bronchoconstrictive signaling, result from the chronic administration of certain 'beta-blockers'.
Figures
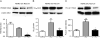
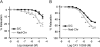
Similar articles
-
Chronic exposure to beta-blockers attenuates inflammation and mucin content in a murine asthma model.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008 Mar;38(3):256-62. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0279RC. Epub 2007 Dec 20. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18096872 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of acute and chronic administration of beta-adrenoceptor ligands on airway function in a murine model of asthma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 6;101(14):4948-53. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400452101. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15069206 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of β-blockers on house dust mite-driven murine models pre- and post-development of an asthma phenotype.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2017 Oct;46:30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28729042 Free PMC article.
-
[Beta blockers in migraine prophylaxis].Brain Nerve. 2009 Oct;61(10):1125-30. Brain Nerve. 2009. PMID: 19882938 Review. Japanese.
-
beta-Adrenoceptor inverse agonists in asthma.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;10(3):254-9. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2010.03.002. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20399707 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alteration of airway responsiveness mediated by receptors in ovalbumin-induced asthmatic E3 rats.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009 Jul;30(7):965-72. doi: 10.1038/aps.2009.61. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2009. PMID: 19575000 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of hydrocortisone on acute β-adrenoceptor blocker and histamine induced bronchoconstriction.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 May;73(5):717-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2011.04143.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22077869 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sorafenib cardiotoxicity increases mortality after myocardial infarction.Circ Res. 2014 May 23;114(11):1700-1712. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.303200. Epub 2014 Apr 9. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 24718482 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-blockers reduced the risk of mortality and exacerbation in patients with COPD: a meta-analysis of observational studies.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 26;9(11):e113048. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113048. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25427000 Free PMC article.
-
β2-adrenoreceptor Inverse Agonist Down-regulates Muscarine Cholinergic Subtype-3 Receptor and Its Downstream Signal Pathways in Airway Smooth Muscle Cells in vitro.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 4;7:39905. doi: 10.1038/srep39905. Sci Rep. 2017. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 06;9(1):4109. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39065-w. PMID: 28051147 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Barnes PJ. Beta-adrenoceptors on smooth muscle, nerves and inflammatory cells. Life Sci. 1993;52(26):2101–9. - PubMed
-
- Rossing TH, Fanta CH, Goldstein DH, Snapper JR, McFadden ER., Jr Emergency therapy of asthma: comparison of the acute effects of parenteral and inhaled sympathomimetics and infused aminophylline. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1980;122(3):365–71. - PubMed
-
- Waldeck B. Beta-adrenoceptor agonists and asthma—100 years of development. Eur J Pharmacol. 2002;445(12):1–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

