Lysophosphatidic acid modulates c-Met redistribution and hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling in human bronchial epithelial cells through PKC delta and E-cadherin
- PMID: 17689924
- PMCID: PMC2149844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.07.005
Lysophosphatidic acid modulates c-Met redistribution and hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling in human bronchial epithelial cells through PKC delta and E-cadherin
Abstract
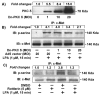
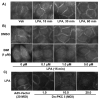
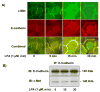
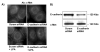
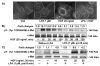
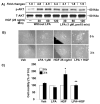
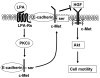
Previously we demonstrated that ligation of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) to G protein-coupled LPA receptors induces transactivation of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs), such as platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta (PDGF-Rbeta) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R), in primary cultures of human bronchial epithelial cells (HBEpCs). Here we examined the role of LPA on c-Met redistribution and modulation of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-Met pathways in HBEpCs. Treatment of HBEpCs with LPA-induced c-Met serine phosphorylation and redistribution to plasma membrane, while treatment with HGF-induced c-Met internalization. Pretreatment with LPA reversed HGF-induced c-Met internalization. Overexpression of dominant negative (Dn)-PKC delta or pretreatment with Rottlerin or Pertussis toxin (PTx) attenuated LPA-induced c-Met serine phosphorylation and redistribution. Co-immnuoprecipitation and immunocytochemistry showed that E-cadherin interacted with c-Met in HBEpCs. LPA treatment induced E-cadherin and c-Met complex redistribution to plasma membranes. Overexpression of Dn-PKC delta attenuated LPA-induced E-cadherin redistribution and E-cadherin siRNA attenuated LPA-induced c-Met redistribution to plasma membrane. Furthermore, pretreatment of LPA attenuated HGF-induced c-Met tyrosine phosphorylation and downstream signaling, such as Akt kinase phosphorylation and cell motility. These results demonstrate that LPA regulates c-Met function through PKC delta and E-cadherin in HBEpCs, suggesting an alternate function of the cross-talk between G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and RTKs in HBEpCs.
Figures

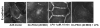
Similar articles
-
Lysophosphatidic acid enhances pulmonary epithelial barrier integrity and protects endotoxin-induced epithelial barrier disruption and lung injury.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24123-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007393. Epub 2009 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19586906 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of lysophosphatidic acid-induced epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation and interleukin-8 secretion in human bronchial epithelial cells by protein kinase Cdelta, Lyn kinase, and matrix metalloproteinases.J Biol Chem. 2006 Jul 14;281(28):19501-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511224200. Epub 2006 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16687414 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid-induced transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor regulates cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E(2) release via C/EBPbeta in human bronchial epithelial cells.Biochem J. 2008 May 15;412(1):153-62. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071649. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18294142 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of phospholipase D2 in lysophosphatidate-induced transactivation of platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta in human bronchial epithelial cells.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 10;278(41):39931-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M302896200. Epub 2003 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12890682
-
Transactivation of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs): Recent insights using luminescence and fluorescence technologies.Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 2021 Feb;16:102-112. doi: 10.1016/j.coemr.2020.10.003. Curr Opin Endocr Metab Res. 2021. PMID: 33748531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lysophosphatidic acid enhances pulmonary epithelial barrier integrity and protects endotoxin-induced epithelial barrier disruption and lung injury.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 4;284(36):24123-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.007393. Epub 2009 Jul 8. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19586906 Free PMC article.
-
Cholinergic receptor pathways involved in apoptosis, cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation.Cell Commun Signal. 2009 Aug 27;7:20. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-7-20. Cell Commun Signal. 2009. PMID: 19712465 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular regulation of lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 trafficking to the cell surface.Cell Signal. 2014 Nov;26(11):2406-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.07.005. Epub 2014 Jul 13. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 25025571 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mechanisms regulating endothelial barrier function in the pulmonary microcirculation.J Physiol. 2019 Feb;597(4):997-1021. doi: 10.1113/JP276245. Epub 2018 Aug 13. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30015354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A blocking peptide stabilizes lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 and promotes lysophosphatidic acid-induced cellular responses.J Cell Biochem. 2021 Aug;122(8):827-834. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29919. Epub 2021 Apr 13. J Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33847006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rompler H, Staubert C, Thor D, Schulz A, Hofreiter M, Schoneberg T. Mol Interv. 2007;7:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Daynes RA, Araneo BA, Hennebold J, Enioutina E, Mu HHJ. Invest Dermatol. 1995;105:14S–19S. - PubMed
-
- Druker J, Liberman AC, Acuna M, Giacomini D, Refojo D, Silberstein S, Pereda MP, Stalla GK, Holsboer F, Arzt E. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1088:297–304. - PubMed
-
- Natarajan K, Berk BC. Methods Mol Biol. 2006;332:51–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

