Expression of interleukin-15 in human skeletal muscle effect of exercise and muscle fibre type composition
- PMID: 17690139
- PMCID: PMC2277063
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.139618
Expression of interleukin-15 in human skeletal muscle effect of exercise and muscle fibre type composition
Abstract
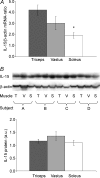
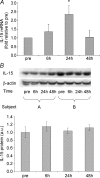
The cytokine interleukin-15 (IL-15) has been demonstrated to have anabolic effects in cell culture systems. We tested the hypothesis that IL-15 is predominantly expressed by type 2 skeletal muscle fibres, and that resistance exercise regulates IL-15 expression in muscle. Triceps brachii, vastus lateralis quadriceps and soleus muscle biopsies were obtained from normally physically active, healthy, young male volunteers (n = 14), because these muscles are characterized by having different fibre-type compositions. In addition, healthy, normally physically active male subjects (n = 8) not involved in any kind of resistance exercise underwent a heavy resistance exercise protocol that stimulated the vastus lateralis muscle and biopsies were obtained from this muscle pre-exercise as well as 6, 24 and 48 h post-exercise. IL-15 mRNA levels were twofold higher in the triceps (type 2 fibre dominance) compared with the soleus muscle (type 1 fibre dominance), but Western blotting and immunohistochemistry revealed that muscle IL-15 protein content did not differ between triceps brachii, quadriceps and soleus muscles. Following resistance exercise, IL-15 mRNA levels were up-regulated twofold at 24 h of recovery without any changes in muscle IL-15 protein content or plasma IL-15 at any of the investigated time points. In conclusion, IL-15 mRNA level is enhanced in skeletal muscles dominated by type 2 fibres and resistance exercise induces increased muscular IL-15 mRNA levels. IL-15 mRNA levels in skeletal muscle were not paralleled by similar changes in muscular IL-15 protein expression suggesting that muscle IL-15 may exist in a translationally inactive pool.
Figures
References
-
- Argiles JM, Lopez-Soriano J, Almendro V, Busquets S, Lopez-Soriano FJ. Cross-talk between skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: a link with obesity? Med Res Rev. 2005;25:49–65. - PubMed
-
- Bamford RN, DeFilippis AP, Azimi N, Kurys G, Waldmann TA. The 5′ untranslated region, signal peptide, and the coding sequence of the carboxyl terminus of IL-15 participate in its multifaceted translational control. J Immunol. 1998;160:4418–4426. - PubMed
-
- Bergstrom J. Percutaneous needle biopsy of skeletal muscle in physiological and clinical research. Scand J Clin Laboratory Invest. 1975;35:609–616. - PubMed
-
- Busquets S, Figueras MT, Meijsing S, Carbo N, Quinn LS, Almendro V, Argiles JM, Lopez-Soriano FJ. Interleukin-15 decreases proteolysis in skeletal muscle: a direct effect. Int J Mol Med. 2005;16:471–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

