Inter-laboratory comparison of chronic myeloid leukemia minimal residual disease monitoring: summary and recommendations
- PMID: 17690211
- PMCID: PMC1975095
- DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2007.060134
Inter-laboratory comparison of chronic myeloid leukemia minimal residual disease monitoring: summary and recommendations
Abstract
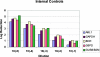
In patients with chronic myeloid leukemia, the use of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) for measuring BCR-ABL1 transcripts has become standard methodology for the diagnosis and monitoring of minimal residual disease. In 2004 and 2005, 38 different laboratories from North America participated in three separate sample exchanges using real-time qRT-PCR to measure RNA transcript levels in unknown diluents of a BCR-ABL1-positive cell line, K562. In this study we compared results of quantitative testing for BCR-ABL1 from laboratories using different platforms, internal controls, reagents, and calculation methods. Our data showed that there can be considerable variability of results from laboratory to laboratory, with log reduction calculations varying from 1.6 to 3 log between laboratories at the same dilution. We found that none of the variables tested had a significant impact on the results reported, except for the use of ABL1 as the internal control (P < 0.001). Laboratories that used ABL1 consistently underreported their log reduction values. Regardless of the specific methodology and platform used for real-time qRT-PCR testing, it is important for laboratories to participate in proficiency testing to ensure consistent and acceptable test accuracy and sensitivity. Our study emphasizes the need for optimization of real-time qRT-PCR before offering clinical testing and the need for widely available universal standards that can be used for test calibration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RT-qPCR and RT-Digital PCR: A Comparison of Different Platforms for the Evaluation of Residual Disease in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Clin Chem. 2017 Feb;63(2):525-531. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.262824. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Clin Chem. 2017. PMID: 27979961
-
Comparison of competitive-nested PCR and real-time PCR in detecting BCR-ABL fusion transcripts in chronic myeloid leukemia patients.Leukemia. 2002 Dec;16(12):2447-53. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2402730. Leukemia. 2002. PMID: 12454751
-
Programme for Harmonization to the International Scale in Latin America for BCR-ABL1 quantification in CML patients: findings and recommendations.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020 Nov 26;58(12):2025-2035. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2019-1283. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32374276
-
A review of the challenge in measuring and standardizing BCR-ABL1.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017 Aug 28;55(10):1465-1473. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2016-0927. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017. PMID: 28222016 Review.
-
Chronic myeloid leukemia: a minimalistic view of post-therapeutic monitoring.J Mol Diagn. 2002 Feb;4(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60675-7. J Mol Diagn. 2002. PMID: 11826183 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in 2015.Mayo Clin Proc. 2015 Oct;90(10):1440-54. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.08.010. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015. PMID: 26434969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality control methods for optimal BCR-ABL1 clinical testing in human whole blood samples.J Mol Diagn. 2013 May;15(3):391-400. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2013.02.004. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Mol Diagn. 2013. PMID: 23541592 Free PMC article.
-
Harmonization of molecular monitoring of chronic myeloid leukemia therapy in Japan.Int J Clin Oncol. 2012 Dec;17(6):584-9. doi: 10.1007/s10147-011-0328-x. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Int J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21986632
-
Understanding the economic value of molecular diagnostic tests: case studies and lessons learned.J Pers Med. 2013 Oct 25;3(4):288-305. doi: 10.3390/jpm3040288. J Pers Med. 2013. PMID: 25562729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guide to interpreting disease responses in chronic myeloid leukemia.J Adv Pract Oncol. 2012 Jul;3(4):225-36. doi: 10.6004/jadpro.2012.3.4.3. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2012. PMID: 25031950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rowley JD. Letter: a new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature. 1973;243:290–293. - PubMed
-
- Shtivelman E, Lifshitz B, Gale RP, Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985;315:550–554. - PubMed
-
- Westbrook CA, Hooberman AL, Spino C, Dodge RK, Larson RA, Davey F, Wurster-Hill DH, Sobol RE, Schiffer C, Bloomfield CD. Clinical significance of the BCR-ABL fusion gene in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study (8762). Blood. 1992;80:2983–2990. - PubMed
-
- Lugo TG, Pendergast AM, Muller AJ, Witte ON. Tyrosine kinase activity and transformation potency of bcr-abl oncogene products. Science. 1990;247:1079–1082. - PubMed
-
- Melo JV. The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia. 1996;10:751–766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

