Conserved P-TEFb-interacting domain of BRD4 inhibits HIV transcription
- PMID: 17690245
- PMCID: PMC1959443
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0705053104
Conserved P-TEFb-interacting domain of BRD4 inhibits HIV transcription
Abstract
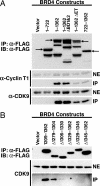
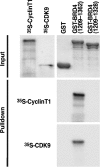
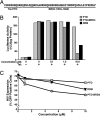
We have identified a conserved region in the C-terminal domain of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) that mediates its specific interaction with positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb). This domain is highly conserved in testis-specific bromodomain protein (BRDT) and Drosophila fs(1)h. Both BRDT and fs(1)h specifically interact with P-TEFb in mammalian cells, and this interaction depends on their C-terminal domains. Overexpression of the BRD4 P-TEFb-interacting domain disrupts the interaction between the HIV transactivator Tat and P-TEFb and suppresses the ability of Tat to transactivate the HIV promoter. Incubation of cells with a synthetic peptide containing the C-terminal domain of BRD4 interferes with transactivation of the HIV promoter by the Tat protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

