Impacts of yeast metabolic network structure on enzyme evolution
- PMID: 17692134
- PMCID: PMC2374984
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-8-407
Impacts of yeast metabolic network structure on enzyme evolution
Abstract
A comment on D Vitkup, P Kharchenko and A Wagner: Influence of metabolic network structure and function on enzyme evolution. Genome Biol 2006, 7:R39.
Figures
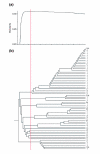
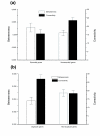
Comment on
-
Influence of metabolic network structure and function on enzyme evolution.Genome Biol. 2006;7(5):R39. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-5-r39. Epub 2006 May 9. Genome Biol. 2006. PMID: 16684370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batagelj V, Mrvar A. Pajek - analysis and visualization of large networks. Connections. 1998;21:47–57.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

