The stimulus-dependent co-localization of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated protein kinase (Sgk) and Erk/MAPK in mammary tumor cells involves the mutual interaction with the importin-alpha nuclear import protein
- PMID: 17692313
- PMCID: PMC3422670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.07.009
The stimulus-dependent co-localization of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated protein kinase (Sgk) and Erk/MAPK in mammary tumor cells involves the mutual interaction with the importin-alpha nuclear import protein
Abstract
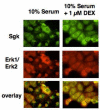
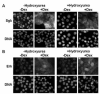
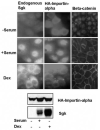
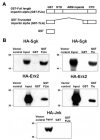
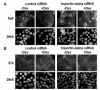
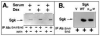
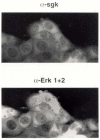
In Con8 rat mammary epithelial tumor cells, indirect immunofluorescence revealed that Sgk (serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase) and Erk/MAPK (extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase/mitogen activated protein kinase) co-localized to the nucleus in serum-treated cells and to the cytoplasmic compartment in cells treated with the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone. Moreover, the subcellular distribution of the importin-alpha nuclear transport protein was similarly regulated in a signal-dependent manner. In vitro GST-pull down assays revealed the direct interaction of importin-alpha with either Sgk or Erk/MAPK, while RNA interference knockdown of importin-alpha expression disrupted the localization of both Sgk and Erk into the nucleus of serum-treated cells. Wild type or kinase dead forms of Sgk co-immunoprecipitated with Erk/MAPK from either serum- or dexamethasone-treated mammary tumor cells, suggesting the existence of a protein complex containing both kinases. In serum-treated cells, nucleus residing Sgk and Erk/MAPK were both hyperphosphorylated, indicative of their active states, whereas, in dexamethasone-treated cells Erk/MAPK, but not Sgk, was in its inactive hypophosphorylated state. Treatment with a MEK inhibitor, which inactivates Erk/MAPK, caused the relocalization of both Sgk and ERK to the cytoplasm. We therefore propose that the signal-dependent co-localization of Sgk and Erk/MAPK mediated by importin-alpha represents a new pathway of signal integration between steroid and serum/growth factor-regulated pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Beato M, Chavez S, Truss M. Transcriptional regulation by steroid hormones. Steroids. 1996;61:240–51. - PubMed
-
- Beato M, Sanchez-Pacheco A. Interaction of steroid hormone receptors with the transcription initiation complex. Endocr. Rev. 1996;17:587–609. - PubMed
-
- Johnson GL, Vaillancourt RR. Sequential protein kinase reactions controlling cell growth and differentiation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1994;6:230–8. - PubMed
-
- Karin M. The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:16483–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

