The proapoptotic factors Bax and Bak regulate T Cell proliferation through control of endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) homeostasis
- PMID: 17692540
- PMCID: PMC2714273
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.05.023
The proapoptotic factors Bax and Bak regulate T Cell proliferation through control of endoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) homeostasis
Abstract
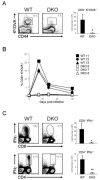
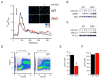
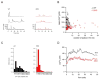
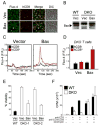
The Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax) and Bcl-2-antagonist/killer (Bak) are essential regulators of lymphocyte apoptosis, but whether they play a role in viable T cell function remains unclear. Here, we report that T cells lacking both Bax and Bak display defects in antigen-specific proliferation because of Ca(2+)-signaling defects. Bax(-/-), Bak(-/-) T cells displayed defective T cell receptor (TCR)- and inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP(3))-dependent Ca(2+) mobilization because of altered endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Ca(2+) regulation that was reversed by Bax's reintroduction. The ability of TCR-dependent Ca(2+) signals to stimulate mitochondrial NADH production in excess of that utilized for ATP synthesis was dependent on Bax and Bak. Blunting of Ca(2+)-induced mitochondrial NADH elevation in the absence of Bax and Bak resulted in decreased reactive-oxygen-species production, which was required for T cell proliferation. Together, the data establish that Bax and Bak play an essential role in the control of T cell proliferation by modulating ER Ca(2+) release.
Figures

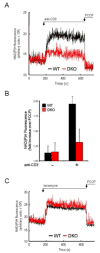
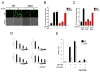
Comment in
-
Revving the engine: signal transduction fuels T cell activation.Immunity. 2007 Aug;27(2):173-8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.07.008. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 17723208
References
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Bidere N, Su HC, Lenardo MJ. Genetic disorders of programmed cell death in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2006;24:321–352. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhri G, Clark IA, Hunt NH, Cowden WB, Ceredig R. Effect of antioxidants on primary alloantigen-induced T cell activation and proliferation. J Immunol. 1986;137:2646–2652. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/B/0000H110/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/B/00001116/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 CA099179/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- BBS/E/B/0000C116/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 GM056328/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

