Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 17692804
- PMCID: PMC2730509
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.07.004
Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma
Abstract
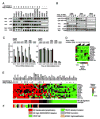
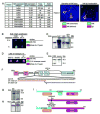
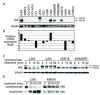
Mechanisms of constitutive NF-kappaB signaling in multiple myeloma are unknown. An inhibitor of IkappaB kinase beta (IKKbeta) targeting the classical NF-kappaB pathway was lethal to many myeloma cell lines. Several cell lines had elevated expression of NIK due to genomic alterations or protein stabilization, while others had inactivating mutations of TRAF3; both kinds of abnormality triggered the classical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways. A majority of primary myeloma patient samples and cell lines had elevated NF-kappaB target gene expression, often associated with genetic or epigenetic alteration of NIK, TRAF3, CYLD, BIRC2/BIRC3, CD40, NFKB1, or NFKB2. These data demonstrate that addiction to the NF-kappaB pathway is frequent in myeloma and suggest that IKKbeta inhibitors hold promise for the treatment of this disease.
Figures





References
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Barlogie B, Shaughnessy J, Tricot G, Jacobson J, Zangari M, Anaissie E, Walker R, Crowley J. Treatment of multiple myeloma. Blood. 2004;103:20–32. - PubMed
-
- Basseres DS, Baldwin AS. Nuclear factor-kappaB and inhibitor of kappaB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene. 2006;25:6817–6830. - PubMed
-
- Berberich I, Shu GL, Clark EA. Cross-linking CD40 on B cells rapidly activates nuclear factor-kappa B. J Immunol. 1994;153:4357–4366. - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Nijman SM, Dirac AM, Bernards R. Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-kappaB. Nature. 2003;424:797–801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

