Down syndrome critical region-1 is a transcriptional target of nuclear factor of activated T cells-c1 within the endocardium during heart development
- PMID: 17693409
- PMCID: PMC2366997
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M703622200
Down syndrome critical region-1 is a transcriptional target of nuclear factor of activated T cells-c1 within the endocardium during heart development
Abstract
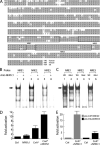
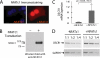
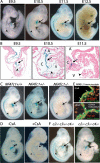
Patients with Down syndrome have characteristic heart valve lesions resulting from endocardial cushion defects. The Down syndrome critical region 1 (DSCR1) gene, identified at the conserved trisomic 21 region in those patients, encodes a calcineurin inhibitor that inactivates nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFATc) activity. Here, we identify a regulatory sequence in the promoter region of human DSCR1 that dictates specific expression of a reporter gene in the endocardium, defined by the temporal and spatial expression of Nfatc1 during heart valve development. Activation of this evolutionally conserved DSCR1 regulatory sequence requires calcineurin and NFATc1 signaling in the endocardium. NFATc1 proteins bind to the regulatory sequence and trigger its enhancer activity. NFATc1 is sufficient to induce the expression of Dscr1 in cells that normally have undetectable or minimal NFATc1 or DSCR1. Pharmacologic inhibition of calcineurin or genetic Nfatc1 null mutation in mice abolishes the endocardial activity of this DSCR1 enhancer. Furthermore, in mice lacking endocardial NFATc1, the endogenous Dscr1 expression is specifically inhibited in the endocardium but not in the myocardium. Thus, our studies indicate that the DSCR1 gene is a direct transcriptional target of NFATc1 proteins within the endocardium during a critical window of heart valve formation.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

