Interactions of the G quartet forming semaphorin 3F RNA with the RGG box domain of the fragile X protein family
- PMID: 17693432
- PMCID: PMC2018618
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm581
Interactions of the G quartet forming semaphorin 3F RNA with the RGG box domain of the fragile X protein family
Abstract
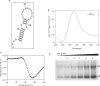
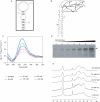
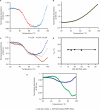
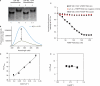
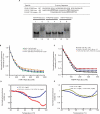
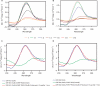
Fragile X syndrome, the most common cause of inherited mental retardation, is caused by the transcriptional silencing of the fmr1 gene due to an unstable expansion of a CGG trinucleotide repeat and its subsequent hypermethylation in its 5' UTR. This gene encodes for the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP), an RNA-binding protein that has been shown to use its RGG box domain to bind to G quartet-forming RNA. In this study, we performed a detailed analysis of the interactions between the FMRP RGG box domain and one of its proposed RNA targets, human semaphorin 3F (S3F) RNA by using biophysical methods such as fluorescence, UV and circular dichroism spectroscopy. We show that this RNA forms a G quartet-containing structure, which is recognized with high affinity and specificity by the FMRP RGG box. In addition, we analyzed the interactions of human S3F RNA with the RGG box and RG cluster of the two FMRP autosomal paralogs, the FXR1P and FXR2P. We found that this RNA is bound with high affinity and specificity only by the FXR1P RGG box, but not by the FXR2P RG cluster. Both FMRP and FXR1P RGG box are able to unwind the G quartet structure of S3F RNA, however, the peptide concentrations required in this process are very different: a ratio of 1:6 RNA:FMRP RGG box versus 1:2 RNA:FXR1P RGG box.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thermodynamics of the fragile X mental retardation protein RGG box interactions with G quartet forming RNA.Biochemistry. 2006 Jul 11;45(27):8319-30. doi: 10.1021/bi060209a. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16819831
-
Analysis of the Fragile X mental retardation protein isoforms 1, 2 and 3 interactions with the G-quadruplex forming semaphorin 3F mRNA.Mol Biosyst. 2012 Feb;8(2):642-9. doi: 10.1039/c1mb05322a. Epub 2011 Dec 1. Mol Biosyst. 2012. PMID: 22134704
-
Fragile X mental retardation protein recognition of G quadruplex structure per se is sufficient for high affinity binding to RNA.Mol Biosyst. 2008 Dec;4(12):1212-9. doi: 10.1039/b812537f. Epub 2008 Oct 27. Mol Biosyst. 2008. PMID: 19396385
-
Biology of the fragile X mental retardation protein, an RNA-binding protein.Biochem Cell Biol. 1999;77(4):331-42. Biochem Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10546896 Review.
-
The fragile X mental retardation protein, FMRP, recognizes G-quartets.Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2004;10(1):49-52. doi: 10.1002/mrdd.20008. Ment Retard Dev Disabil Res Rev. 2004. PMID: 14994288 Review.
Cited by
-
G-Quadruplexes in Neurobiology and Virology: Functional Roles and Potential Therapeutic Approaches.JACS Au. 2021 Nov 22;1(12):2146-2161. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.1c00451. eCollection 2021 Dec 27. JACS Au. 2021. PMID: 34977886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G quadruplex RNA structures in PSD-95 mRNA: potential regulators of miR-125a seed binding site accessibility.RNA. 2015 Jan;21(1):48-60. doi: 10.1261/rna.046722.114. Epub 2014 Nov 18. RNA. 2015. PMID: 25406362 Free PMC article.
-
CGG repeats in the human FMR1 gene regulate mRNA localization and cellular stress in developing neurons.Cell Rep. 2024 Jun 25;43(6):114330. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114330. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38865241 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant bacterial expression and purification of human fragile X mental retardation protein isoform 1.Protein Expr Purif. 2010 Dec;74(2):242-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2010.06.002. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Protein Expr Purif. 2010. PMID: 20541608 Free PMC article.
-
From FMRP function to potential therapies for fragile X syndrome.Neurochem Res. 2014 Jun;39(6):1016-31. doi: 10.1007/s11064-013-1229-3. Epub 2013 Dec 18. Neurochem Res. 2014. PMID: 24346713 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- O’Donnell WT, Warren ST. A decade of molecular studies of fragile x syndrome. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2002;25:315–338. - PubMed
-
- Jin P, Warren ST. Understanding the molecular basis of fragile X syndrome. Hum. Mol. Gen. 2000;6:901–908. - PubMed
-
- Ashley CT, Wilkinson KD, Reines D, Warren ST. FMR1 protein: conserved RNP family domains and selective RNA binding. Science. 1993;262:563–566. - PubMed
-
- Antar LN, Bassell GJ. Sunrise at the synapse: the FMRP mRNP shaping the synaptic interface. Neuron. 2003;37:555–558. - PubMed

