Ligand-induced folding of the thiM TPP riboswitch investigated by a structure-based fluorescence spectroscopic approach
- PMID: 17693433
- PMCID: PMC2018614
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm580
Ligand-induced folding of the thiM TPP riboswitch investigated by a structure-based fluorescence spectroscopic approach
Abstract
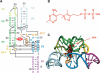
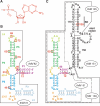
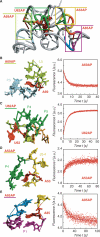
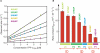
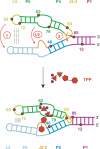
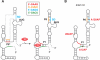
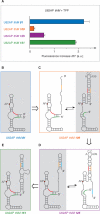
Riboswitches are genetic control elements within non-coding regions of mRNA. They consist of a metabolite-sensitive aptamer and an adjoining expression platform. Here, we describe ligand-induced folding of a thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) responsive riboswitch from Escherichia coli thiM mRNA, using chemically labeled variants. Referring to a recent structure determination of the TPP/aptamer complex, each variant was synthesized with a single 2-aminopurine (AP) nucleobase replacement that was selected to monitor formation of tertiary interactions of a particular region during ligand binding in real time by fluorescence experiments. We have determined the rate constants for conformational adjustment of the individual AP sensors. From the 7-fold differentiation of these constants, it can be deduced that tertiary contacts between the two parallel helical domains (P2/J3-2/P3/L3 and P4/P5/L5) that grip the ligand's ends in two separate pockets, form significantly faster than the function-critical three-way junction with stem P1 fully developed. Based on these data, we characterize the process of ligand binding by an induced fit of the RNA and propose a folding model of the TPP riboswitch aptamer. For the full-length riboswitch domain and for shorter constructs that represent transcriptional intermediates, we have additionally evaluated ligand-induced folding via AP-modified variants and provide insights into the sequential folding pathway that involves a finely balanced equilibrium of secondary structures.
Figures
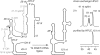
References
-
- Mandal M, Breaker RR. Gene regulation by riboswitches. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;5:451–463. - PubMed
-
- Winkler WC, Breaker RR. Genetic control by metabolite-binding riboswitches. Chembiochem. 2003;4:1024–1032. - PubMed
-
- Soukup JK, Soukup GA. Riboswitches exert genetic control through metabolite-induced conformational change. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2004;14:344–349. - PubMed
-
- Sashital DG, Butcher SE. Flipping off the riboswitch: RNA structures that control gene expression. ACS Chem. Biol. 2006;1:341–345. - PubMed
-
- Nudler E, Mironov AS. The riboswitch control of bacterial metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004;29:11–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

