Thermodynamically modulated partially double-stranded linear DNA probe design for homogeneous real-time PCR
- PMID: 17693434
- PMCID: PMC2018630
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkm551
Thermodynamically modulated partially double-stranded linear DNA probe design for homogeneous real-time PCR
Abstract
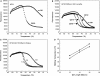
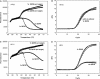
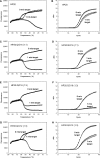
Real-time PCR assays have recently been developed for diagnostic and research purposes. Signal generation in real-time PCR is achieved with probe designs that usually depend on exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase (e.g. TaqMan probe) or oligonucleotide hybridization (e.g. molecular beacon). Probe design often needs to be specifically tailored either to tolerate or to differentiate between sequence variations. The conventional probe technologies offer limited flexibility to meet these diverse requirements. Here, we introduce a novel partially double-stranded linear DNA probe design. It consists of a hybridization probe 5'-labeled with a fluorophore and a shorter quencher oligo of complementary sequence 3'-labeled with a quencher. Fluorescent signal is generated when the hybridization probe preferentially binds to amplified targets during PCR. This novel class of probe can be thermodynamically modulated by adjusting (i) the length of hybridization probe, (ii) the length of quencher oligo, (iii) the molar ratio between the two strands and (iv) signal detection temperature. As a result, pre-amplification signal, signal gain and the extent of mismatch discrimination can be reliably controlled and optimized. The applicability of this design strategy was demonstrated in the Abbott RealTime HIV-1 assay.
Figures
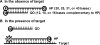



Similar articles
-
Partially double-stranded linear DNA probes: novel design for sensitive detection of genetically polymorphic targets.J Virol Methods. 2007 Sep;144(1-2):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2007.03.009. Epub 2007 Apr 16. J Virol Methods. 2007. PMID: 17434605
-
Symmetric vs asymmetric PCR and molecular beacon probe in the detection of a target gene of adenovirus.Mol Cell Probes. 2000 Feb;14(1):25-32. doi: 10.1006/mcpr.1999.0278. Mol Cell Probes. 2000. PMID: 10722789
-
Hybridization kinetics of double-stranded DNA probes for rapid molecular analysis.Analyst. 2009 Aug;134(8):1675-81. doi: 10.1039/b906077d. Epub 2009 May 22. Analyst. 2009. PMID: 20448937
-
[Quantitative PCR in the diagnosis of Leishmania].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):163-7. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305709 Review. Italian.
-
Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of mitochondrial DNA point mutation.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;335:187-200. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-069-3:187. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16785629 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Target Strategy for Pan/Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus (FMDV) Detection: A Combination of Sequences Analysis, in Silico Predictions and Laboratory Diagnostic Evaluation.Front Vet Sci. 2018 Jul 12;5:160. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00160. eCollection 2018. Front Vet Sci. 2018. PMID: 30050913 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Abbott m2000 RealTime human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) assay for HIV load monitoring in South Africa compared to the Roche Cobas AmpliPrep-Cobas Amplicor, Roche Cobas AmpliPrep-Cobas TaqMan HIV-1, and BioMerieux NucliSENS EasyQ HIV-1 assays.J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Jul;47(7):2209-17. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01761-08. Epub 2009 May 6. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19420172 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of the new Roche Cobas AmpliPrep-Cobas TaqMan version 2.0 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 assay.J Clin Microbiol. 2009 Oct;47(10):3400-2. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00727-09. Epub 2009 Aug 5. J Clin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19656975 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Evaluation of the Abbott investigational use only realtime HIV-1 assay and comparison to the Roche Amplicor HIV-1 monitor test, version 1.5.J Mol Diagn. 2009 Jul;11(4):347-54. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2009.080166. Epub 2009 May 21. J Mol Diagn. 2009. PMID: 19460935 Free PMC article.
-
An elegant biosensor molecular beacon probe: challenges and recent solutions.Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:928783. doi: 10.6064/2012/928783. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 24278758 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bustin SA, Mueller R. Real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and its potential use in clinical diagnosis. Cln. Sci. (Lond) 2005;109:365–379. - PubMed
-
- Mackay IM. Real-time PCR in the microbiology laboratory. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004;10:190–212. - PubMed
-
- Bernard PS, Wittwer CT. Real-time PCR technology for cancer diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 2002;48:1178–1185. - PubMed
-
- Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D, Decallonne B, Bouillon R, Mathieu C. An overview of real-time quantitative PCR: applications to quantify cytokine gene expression. Methods. 2001;25:386–401. - PubMed
-
- Kurrasch DM, Huang J, Wilkie TM, Repa JJ. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction measurement of regulators of G-protein signaling mRNA levels in mouse tissues. Methods Enzymol. 2004;389:3–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

